Ch03_DataStructure
Yang Haoran 12/14/2022 Go
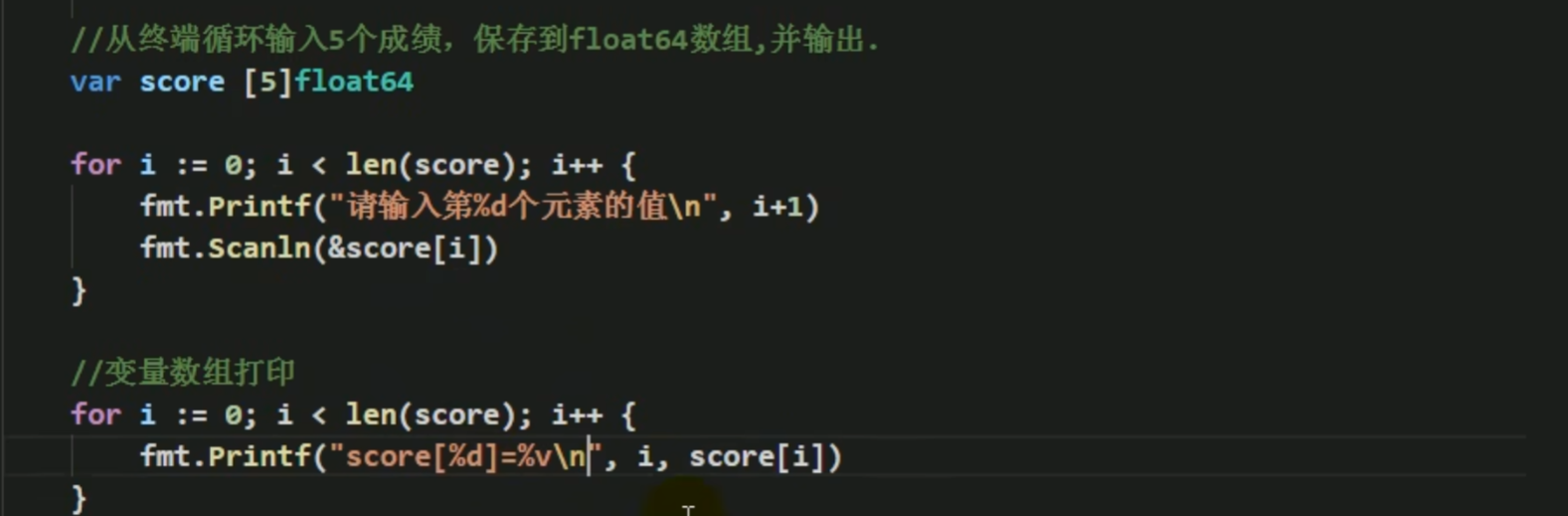
# Array
数组是值传递
声明数组
var balance [10] float32
1
初始化数组
var balance = [5]float32{1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 7.0, 50.0}
or
balance := [5]float32{1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 7.0, 50.0}
1
2
3
2
3
数组长度不确定
var balance = [...]float32{1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 7.0, 50.0}
或
balance := [...]float32{1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 7.0, 50.0}
1
2
3
2
3
通过下标初始化数组
// 将索引为 1 和 3 的元素初始化
balance := [5]float32{1:2.0,3:7.0}
1
2
2
向数组中添加元素
var balance []float32
balance = append(balance, 3.0)
balance = append(balance, 4.0)
fmt.Println(balance)
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
二维数组
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// 创建空的二维数组
animals := [][]string{}
// 创建三一维数组,各数组长度不同
row1 := []string{"fish", "shark", "eel"}
row2 := []string{"bird"}
row3 := []string{"lizard", "salamander"}
// 使用 append() 函数将一维数组添加到二维数组中
animals = append(animals, row1)
animals = append(animals, row2)
animals = append(animals, row3)
// 循环输出
for index,value := range animals {
fmt.Printf("Row: %v\n", index)
fmt.Println(value)
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
占位符:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39386145/article/details/125543243
# 空指针判断
类型前的*是声明这是个指针
&取地址
*取值
if(ptr != nil) /* ptr 不是空指针 */
if(ptr == nil) /* ptr 是空指针 */
1
2
2
# Struct
package main
import "fmt"
type Books struct {
title string
author string
subject string
book_id int
}
func main() {
// 创建一个新的结构体
fmt.Println(Books{"Go 语言", "www.runoob.com", "Go 语言教程", 6495407})
// 也可以使用 key => value 格式
fmt.Println(Books{title: "Go 语言", author: "www.runoob.com", subject: "Go 语言教程", book_id: 6495407})
// 忽略的字段为 0 或 空
fmt.Println(Books{title: "Go 语言", author: "www.runoob.com"})
//用.访问结构体成员
fmt.Printf( "Book 1 title : %s\n", Book1.title)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
作为函数参数
package main
import "fmt"
type Books struct {
title string
author string
subject string
book_id int
}
func main() {
var Book1 Books /* 声明 Book1 为 Books 类型 */
var Book2 Books /* 声明 Book2 为 Books 类型 */
/* book 1 描述 */
Book1.title = "Go 语言"
Book1.author = "www.runoob.com"
Book1.subject = "Go 语言教程"
Book1.book_id = 6495407
/* book 2 描述 */
Book2.title = "Python 教程"
Book2.author = "www.runoob.com"
Book2.subject = "Python 语言教程"
Book2.book_id = 6495700
/* 打印 Book1 信息 */
printBook(Book1)
/* 打印 Book2 信息 */
printBook(Book2)
}
func printBook( book Books ) {
fmt.Printf( "Book title : %s\n", book.title)
fmt.Printf( "Book author : %s\n", book.author)
fmt.Printf( "Book subject : %s\n", book.subject)
fmt.Printf( "Book book_id : %d\n", book.book_id)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
嵌套
import "fmt"
type person struct {
name string
age int
}
type student struct {
p1 person
num int
}
func main() {
fmt.Println(student{person{"yang", 77}, 1})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
- 结构体的所有字段在内存中是连续的
- 结构体一般是值传递,除非用*ptr结构体指针
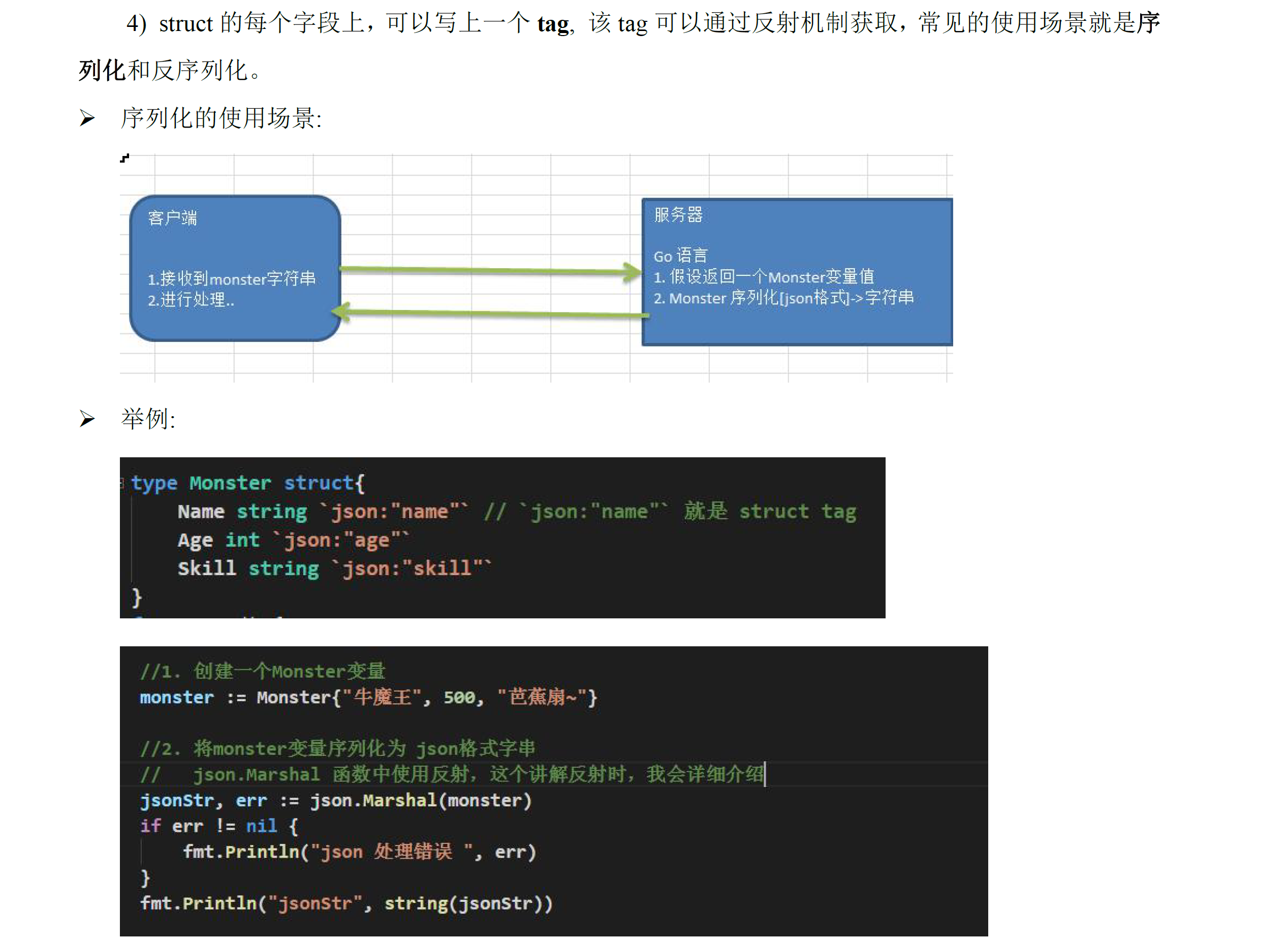
# 序列化反序列化
变量名要大写
type person struct {
Name string `json:"nameaaa"`
Age int `json:"ageaaaa"`
}
func main() {
p1 := person{"yang", 23}
var str, err = json.Marshal(p1)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
} else {
fmt.Println(string(str)) //{"nameaaa":"yang","ageaaaa":23}
}
var p2 = &person{}
json.Unmarshal([]byte(string(str)), p2)
fmt.Println(p2.Age)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
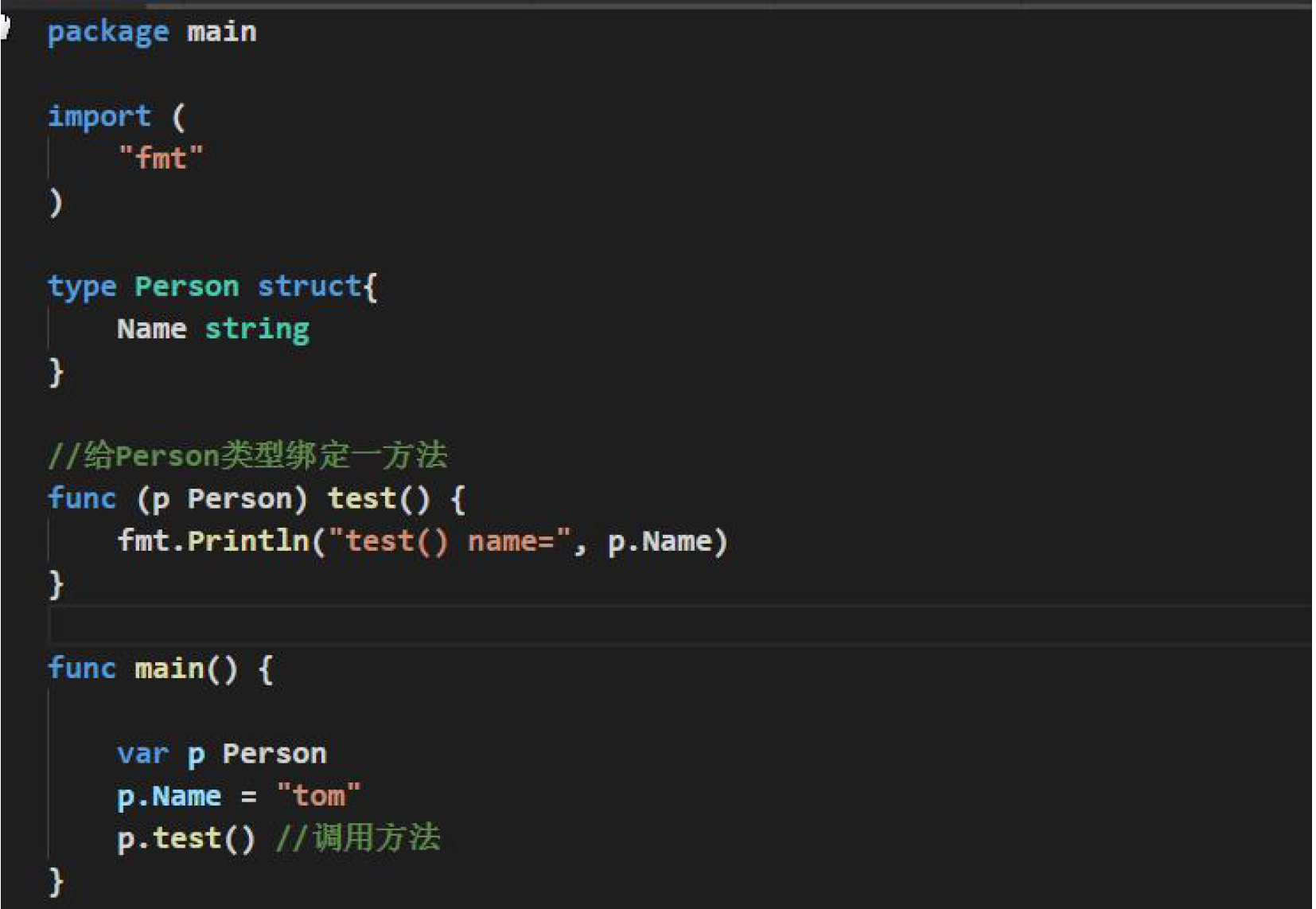
# Struct方法的定义
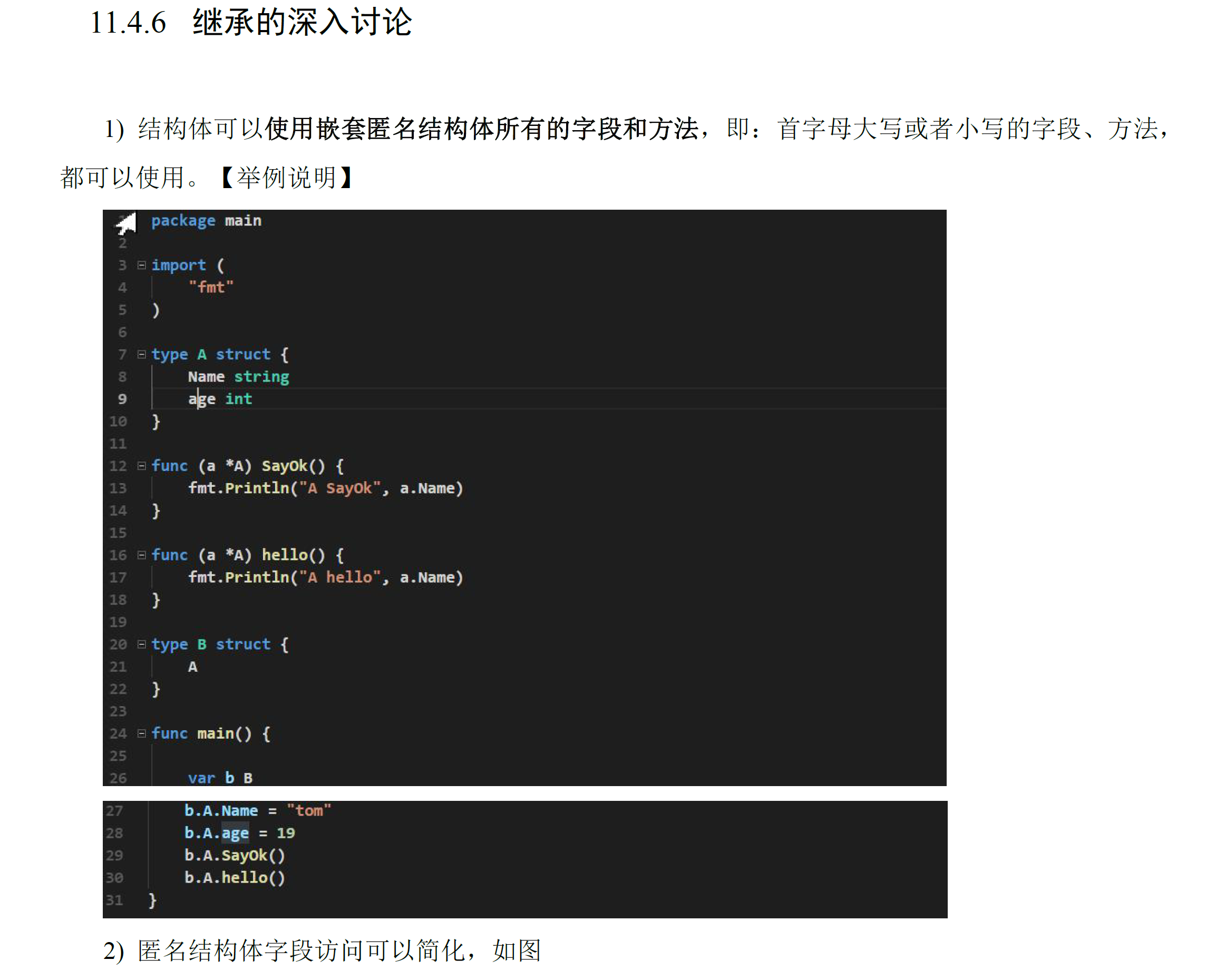
# 继承
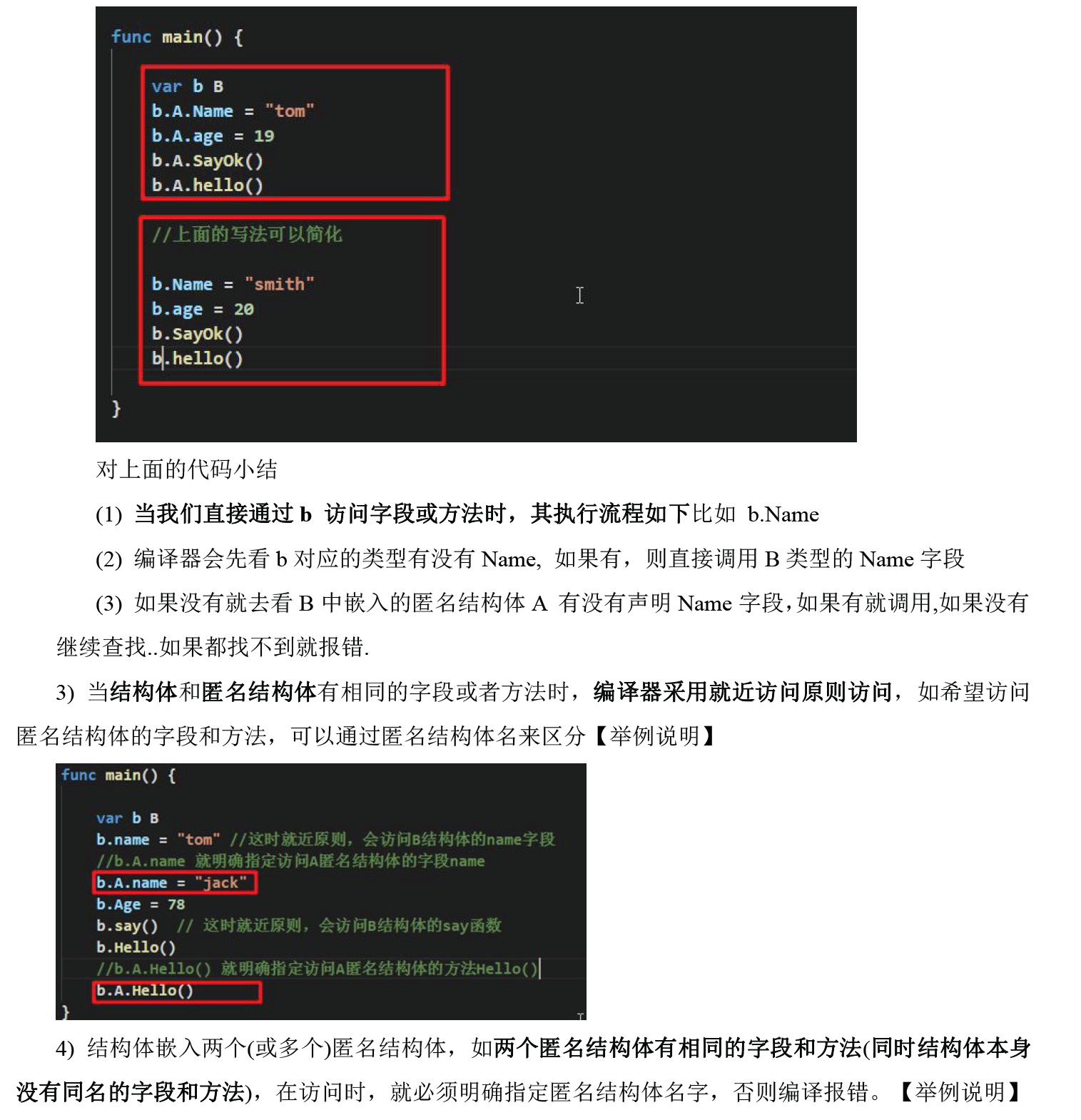
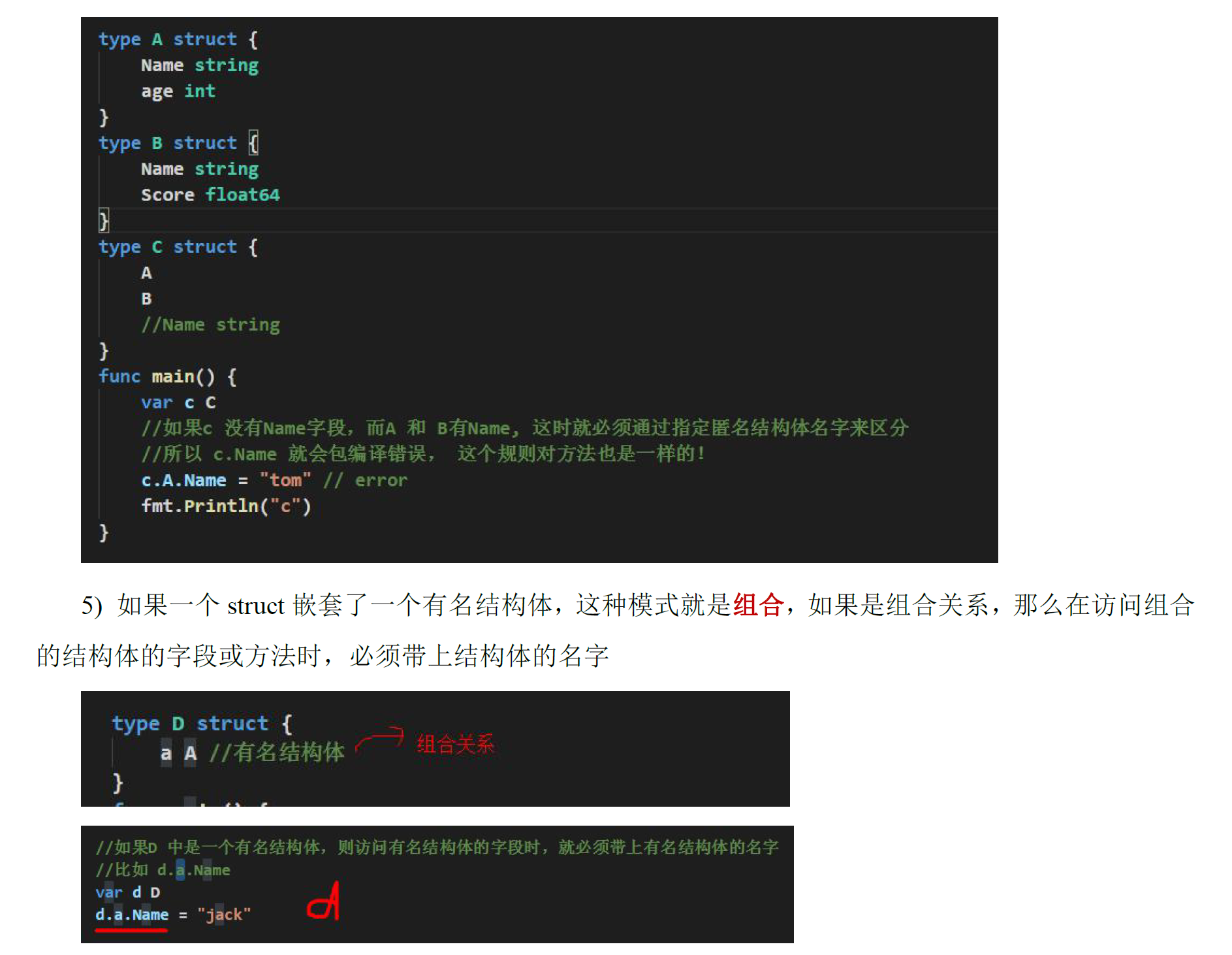
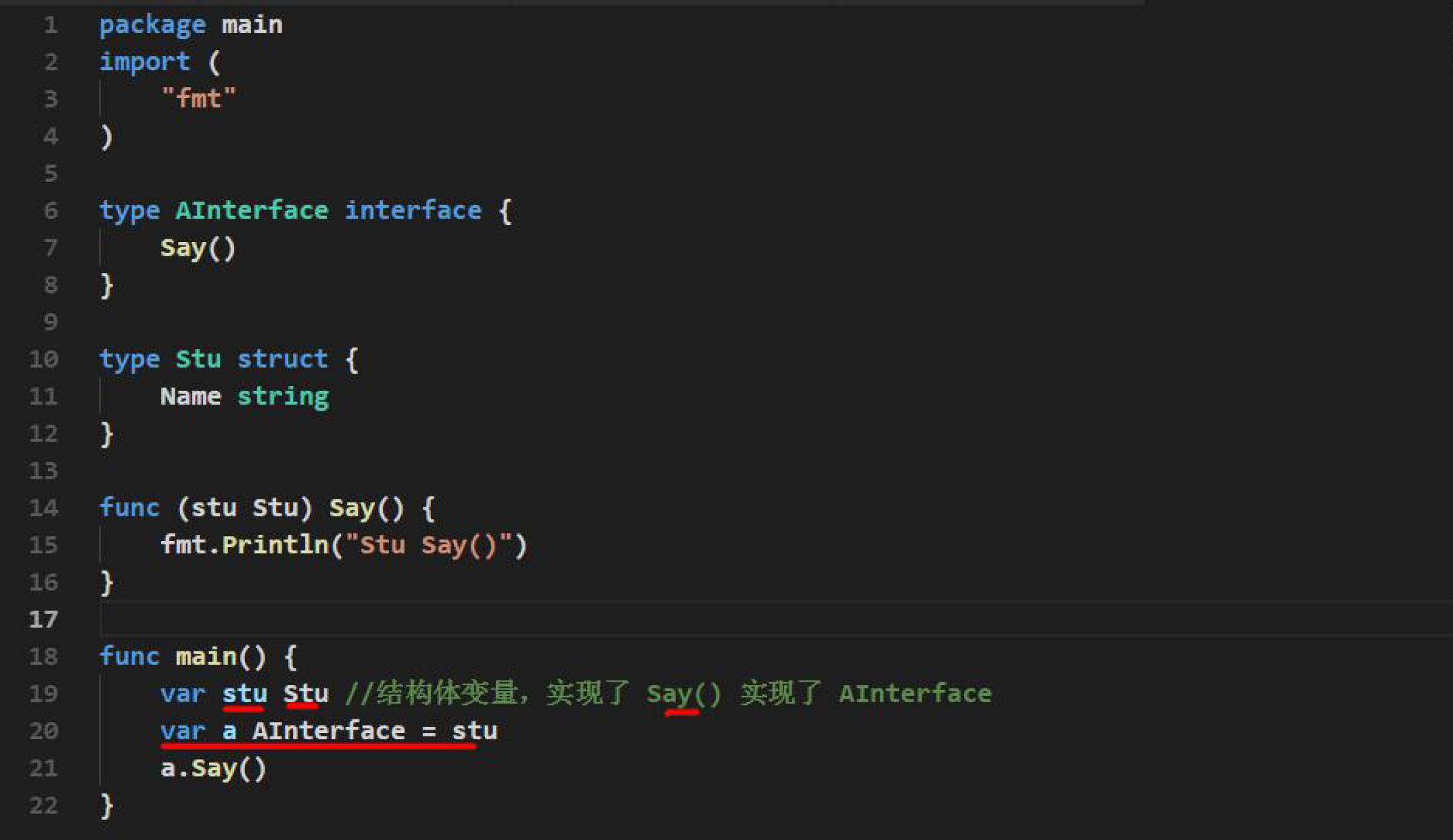
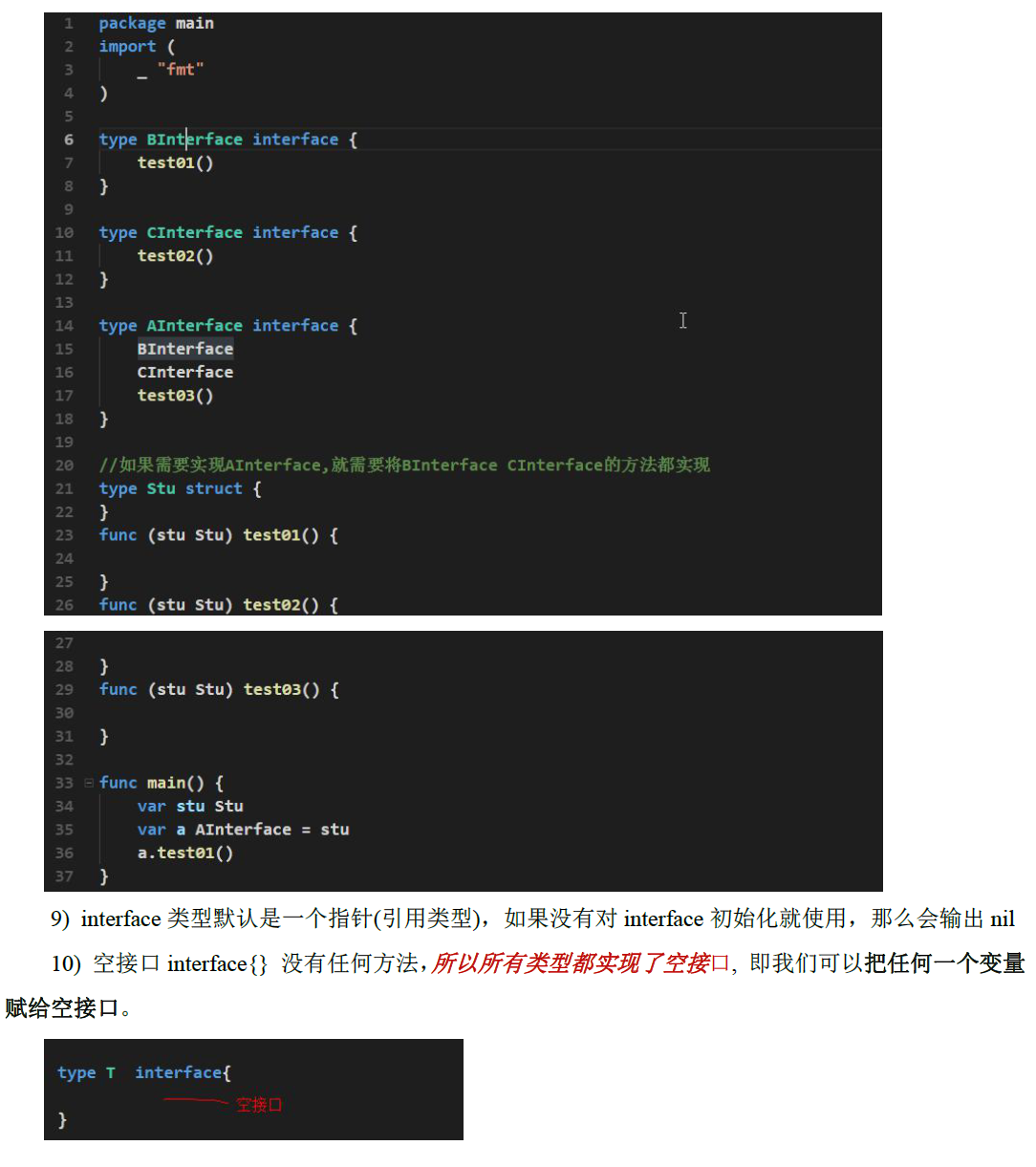
# 接口

# Slice
指定大小是数组,不指定大小是切片
是引用传递的

len:长度大小
cap:容量大小
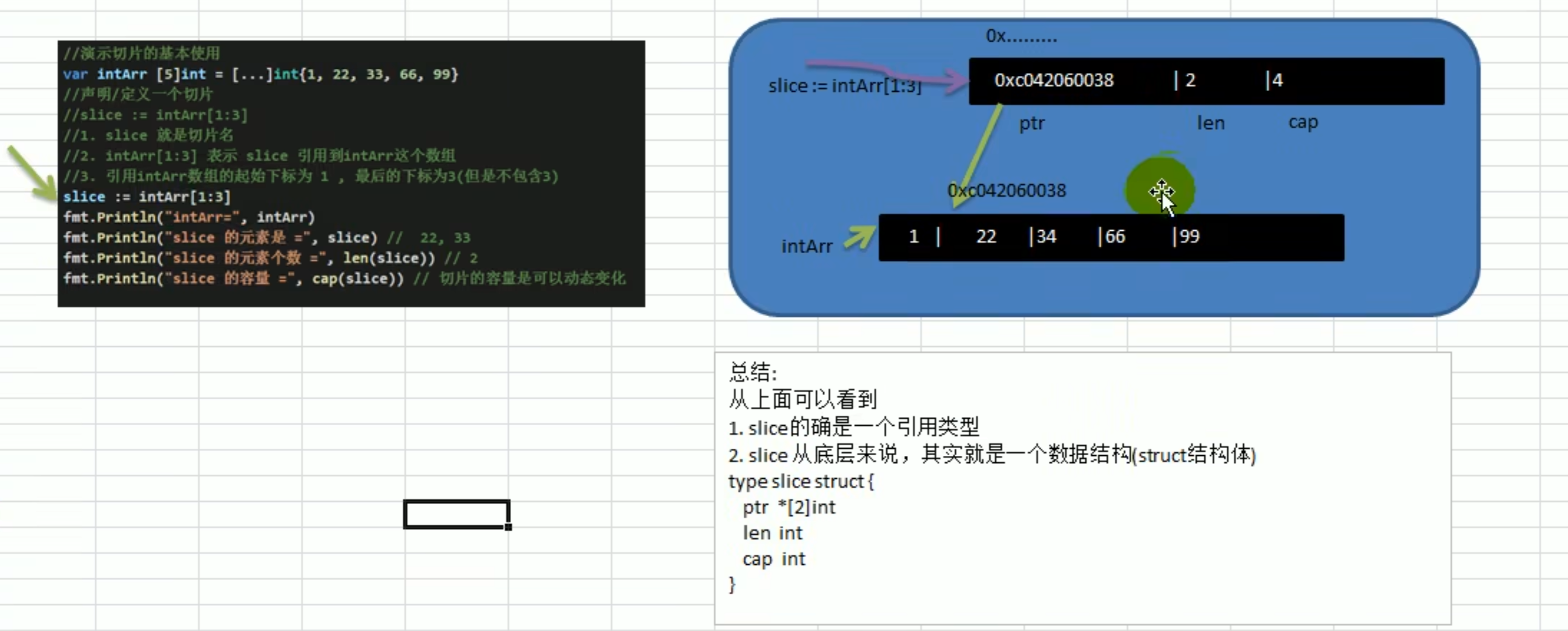
- 既可以通过slice来维护,又可以通过数组来维护
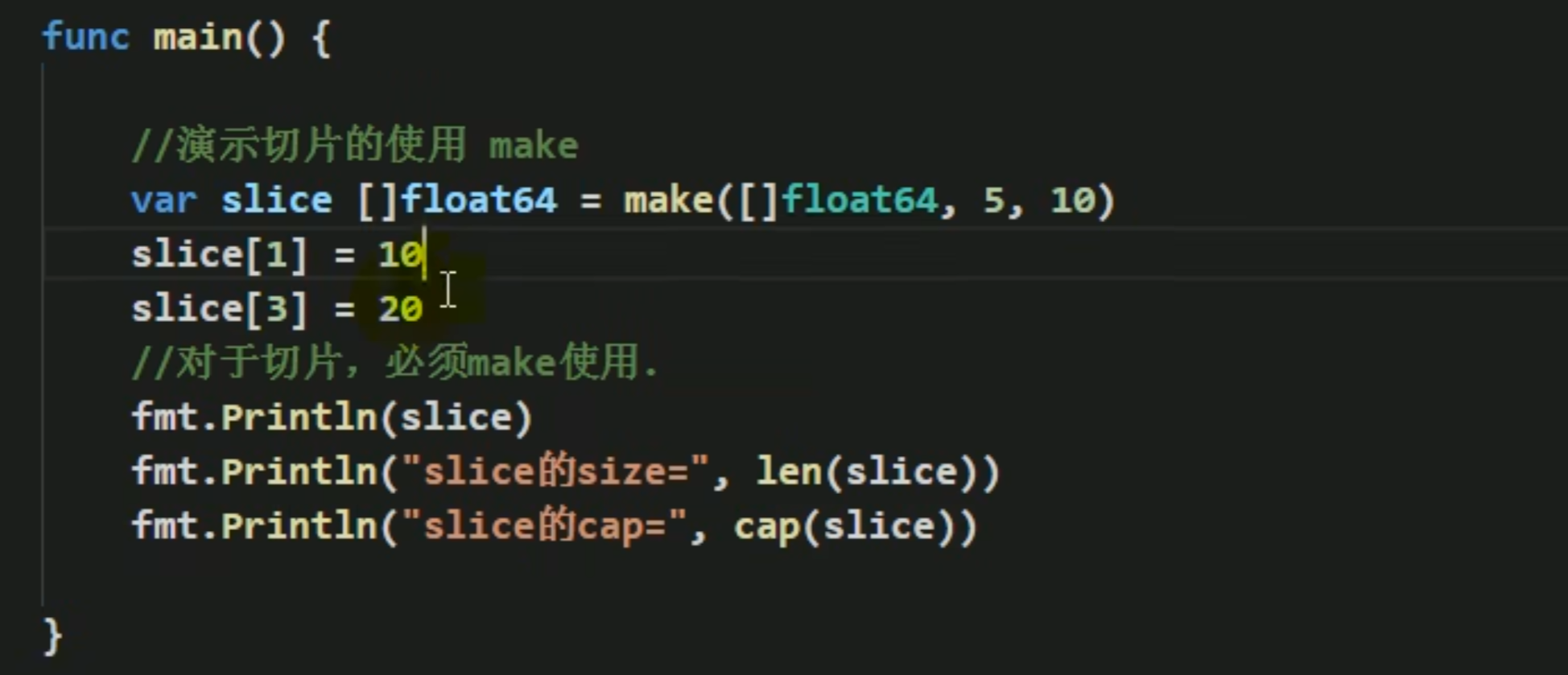

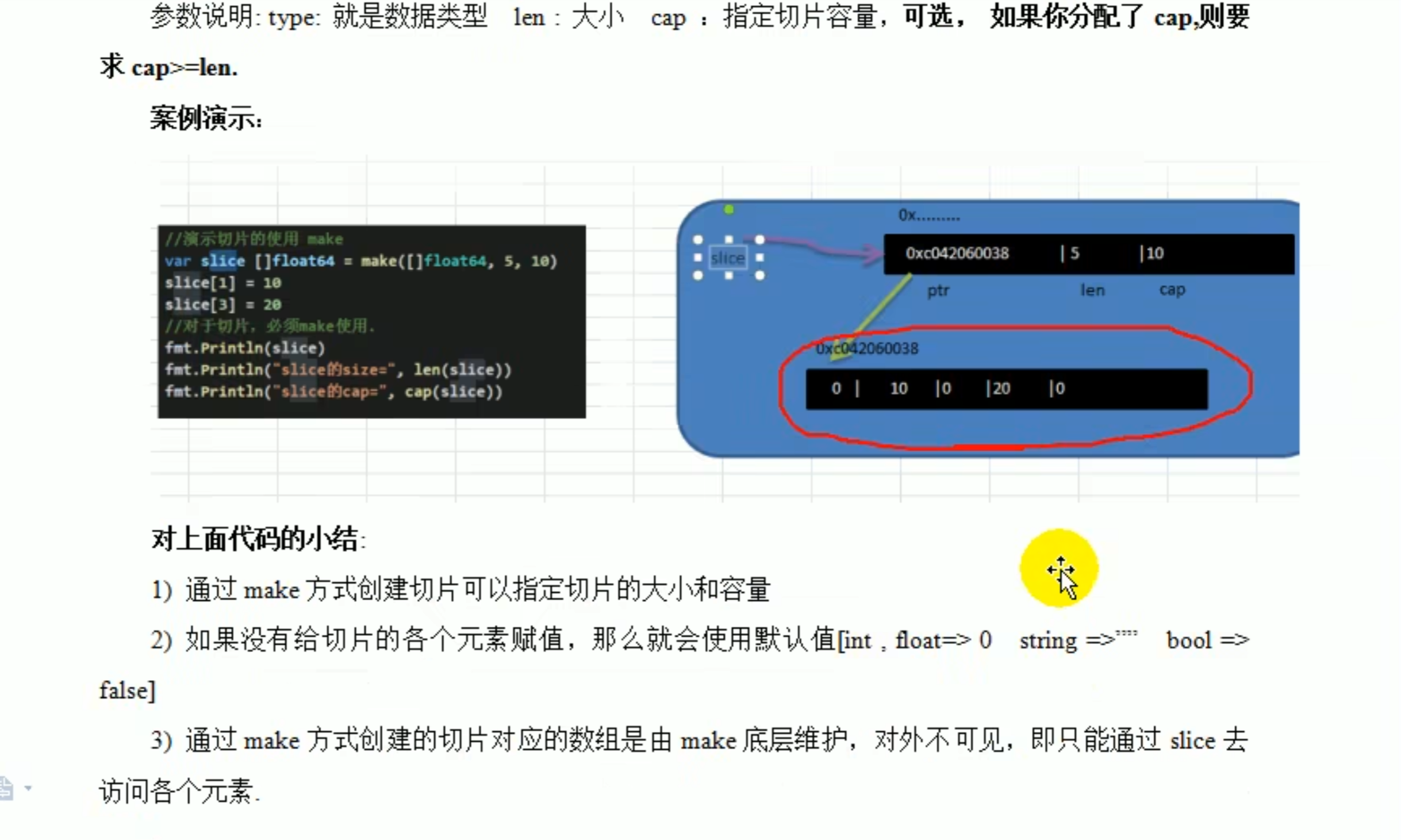
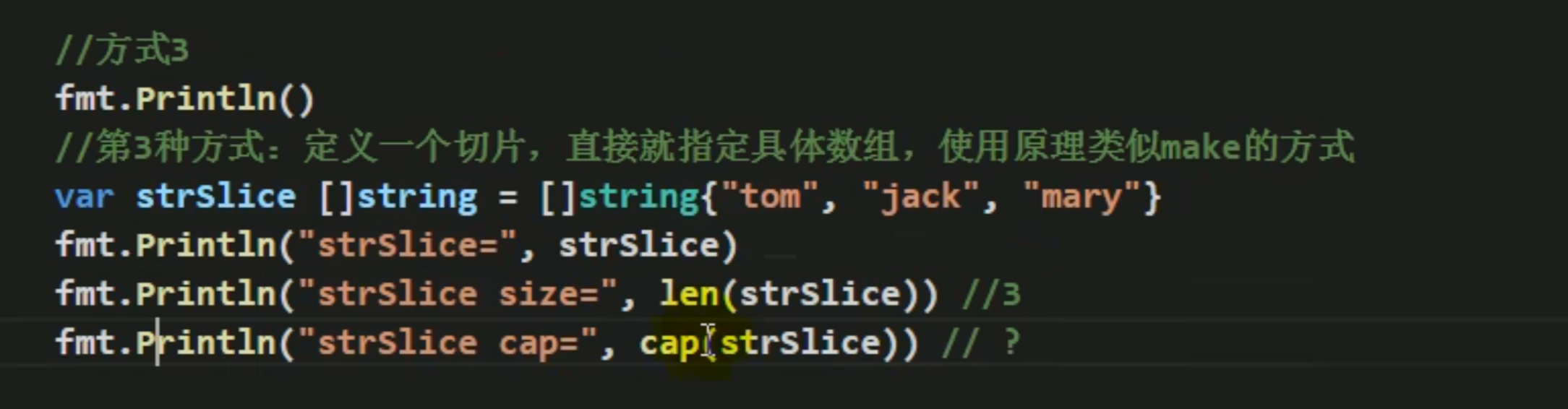


遍历
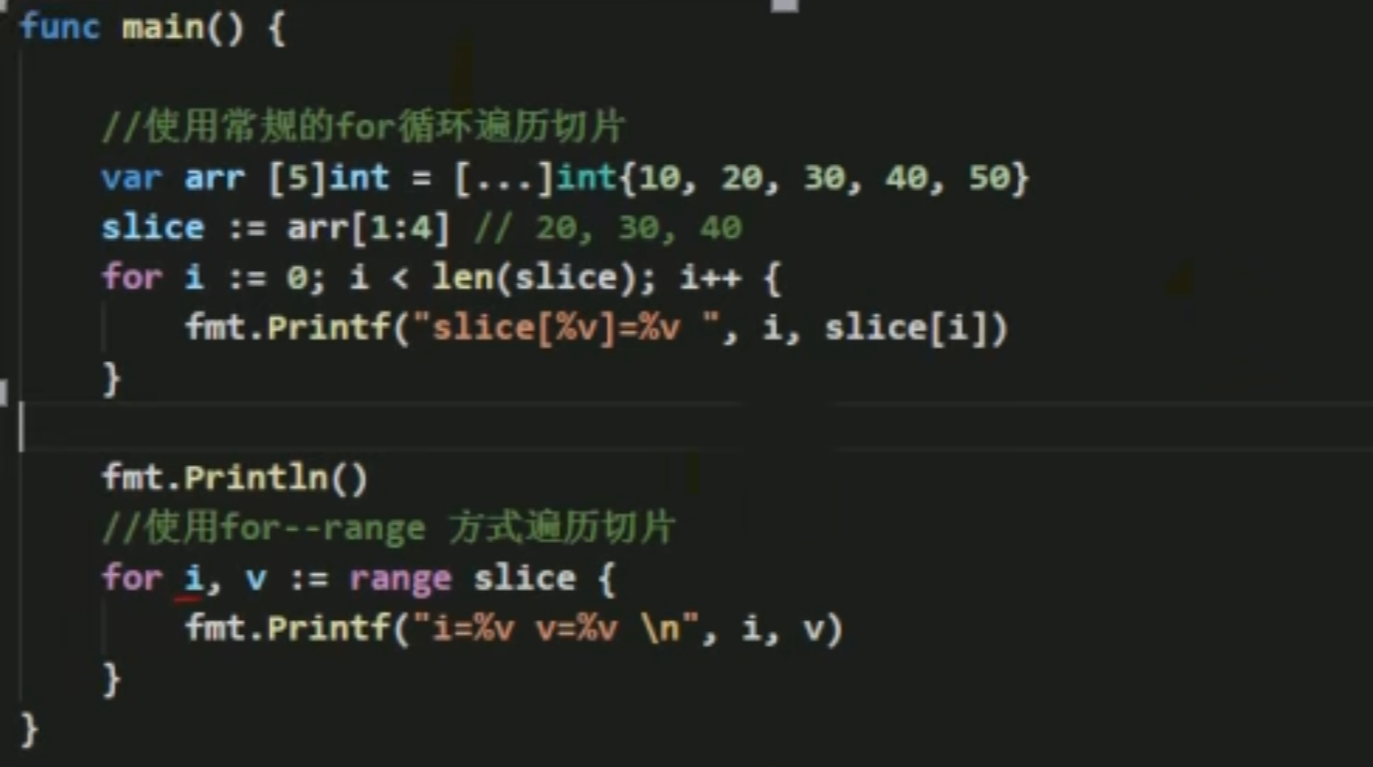

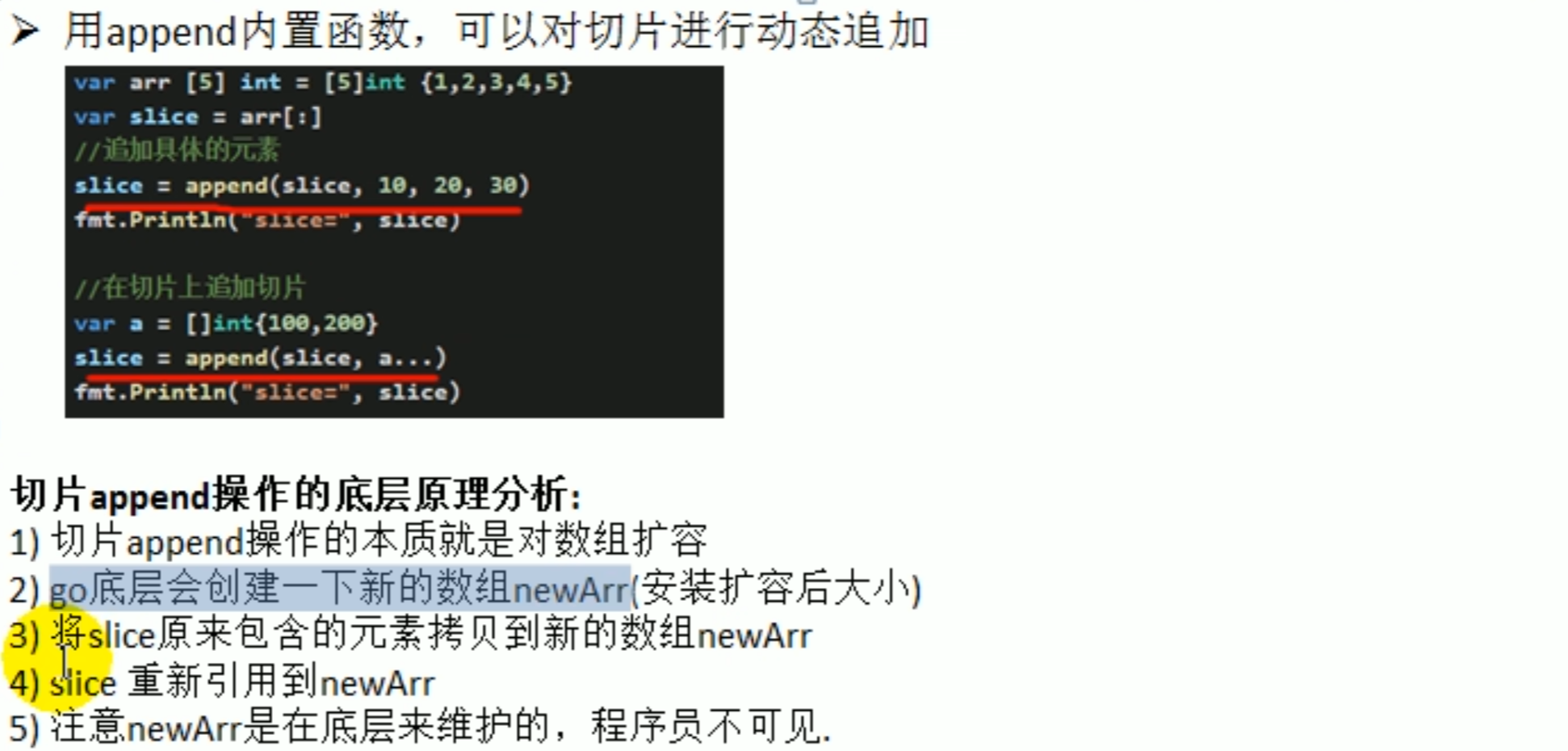
copy:

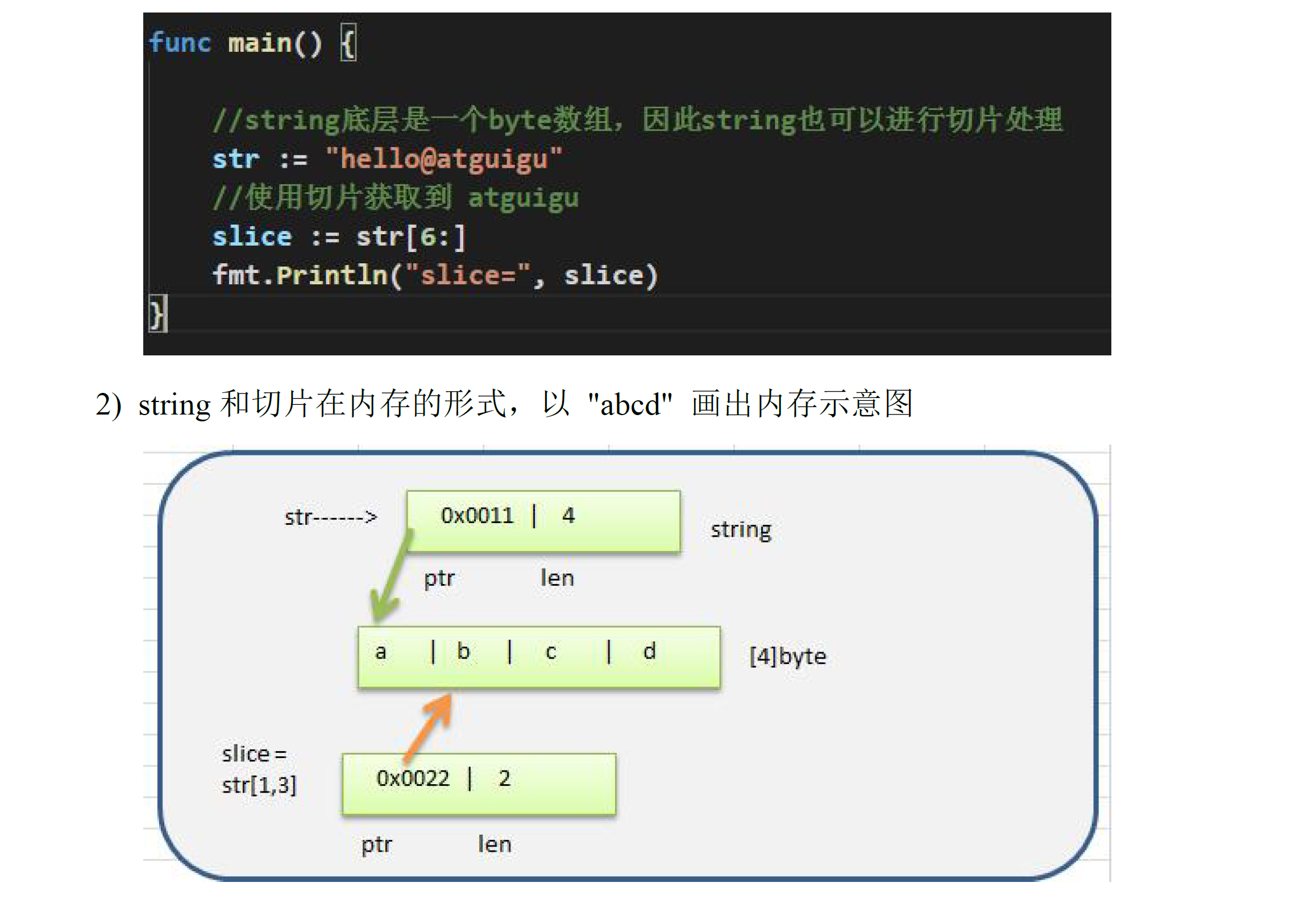
# String
String也可以切片处理
# Map
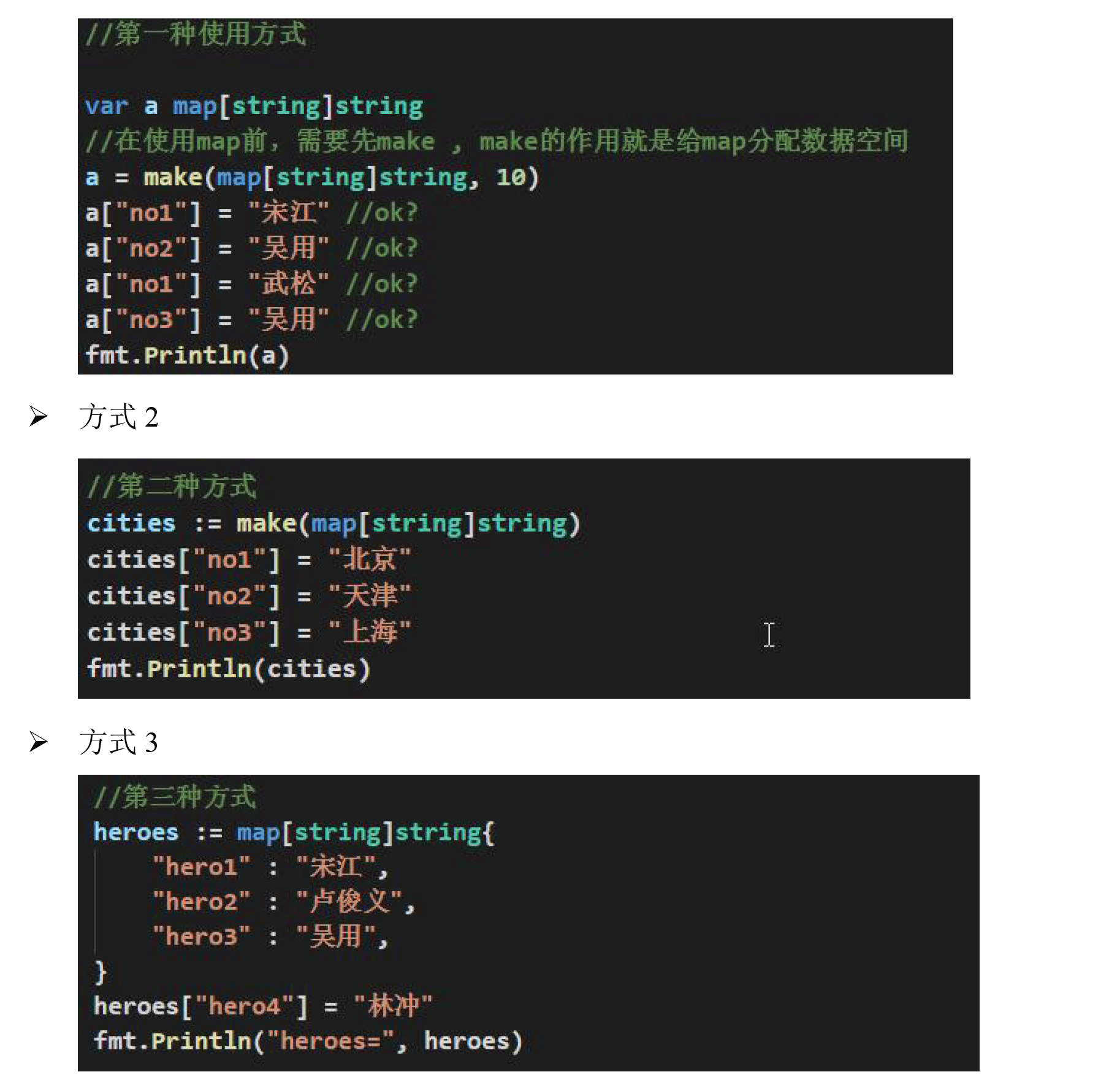
map的增加和更新:map[key] = value, 当key相同的时候更新
删除:delete(map, key)
查询:
var value, ok = a["yyy"] fmt.Println(value) // hhhh fmt.Println(ok) // true1
2
3遍历
for k, v := range a { fmt.Printf("k=%v, v=%v", k, v) }1
2
3map是引用类型
