Ch02 HashTable
Yang Haoran 7/8/2023 List
# HashTable
# HashSet
HashSet 基于 HashMap 来实现的,是一个不允许有重复元素的集合,线程不安全
常用方法:
创建
import java.util.HashSet; // 引入 HashSet 类 HashSet<String> sites = new HashSet<String>();1
2增加,删除,获取元素, 遍历
HashSet<String> sites = new HashSet<String>(); sites.add("Google"); sites.add("Runoob"); sites.add("Taobao"); sites.add("Zhihu"); sites.add("Runoob"); // 重复的元素不会被添加 System.out.println(sites.contains("Taobao"));// 元素是否存在 sites.remove("Taobao"); // 删除元素,删除成功返回 true,否则为 false sites.clear(); //删除所有元素 System.out.println(sites.size()); //大小 for (String i : sites) { System.out.println(i); }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# HashMap
是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射。
常用方法:
创建
import java.util.HashMap; // 引入 HashMap 类 HashMap<Integer, String> Sites = new HashMap<Integer, String>();1
2增加,删除,获取元素, 遍历
HashMap<Integer, String> Sites = new HashMap<Integer, String>(); // 添加键值对 Sites.put(1, "Google"); Sites.put(2, "Runoob"); Sites.put(3, "Taobao"); Sites.put(4, "Zhihu"); System.out.println(Sites.get(3)); Sites.remove(4); Sites.clear(); System.out.println(Sites.size()); //遍历 // 输出 key 和 value for (Integer i : Sites.keySet()) { System.out.println("key: " + i + " value: " + Sites.get(i)); } // 返回所有 value 值 for(String value: Sites.values()) { // 输出每一个value System.out.print(value + ", "); } PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((pair1, pair2)->pair2[1] - pair1[1]); //注意Map. for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry: map.entrySet()){ int[] toAdd = new int[2]; toAdd[0] = entry.getKey(); toAdd[1] = entry.getValue(); pq.add(toAdd); } containsKey(1); containsValue("Zhihu");1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
String 转char[]: char[] schar = s.toCharArray();
获取某一个位置的char: s.charAt(i);
注意两个长度获取不一样:
s.length();
schar.length;
1
2
2
# 242. 有效的字母异位词

class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
int[] sArray = new int[26];
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
sArray[s.charAt(i) - 'a'] ++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++){
sArray[t.charAt(i) - 'a'] --;
}
for(int i = 0; i < sArray.length; i++){
if(sArray[i] != 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 349. 两个数组的交集

class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
HashSet<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<Integer>();
HashSet<Integer> resultSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
for(int i: nums1){
set1.add(i);
}
for(int i: nums2){
if(set1.contains(i)){
resultSet.add(i);
}
}
int[] result = new int[resultSet.size()];
int j = 0;
for(int i: resultSet){
result[j++] = i;
}
return result;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 202. 快乐数

class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
HashSet<Integer> helpSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
int tmp = getNextNum(n);
while(!helpSet.contains(tmp)){
helpSet.add(tmp);
tmp = getNextNum(tmp);
}
return tmp == 1;
}
public int getNextNum(int n){
int tmp = n;
int result = 0;
while(tmp != 0){
int a = tmp % 10;
result += a * a;
tmp = tmp / 10;
}
return result;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 1. 两数之和

暴力:
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++){
if(nums[i] + nums[j] == target && i != j){
return new int[]{i, j};
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
使用hashmap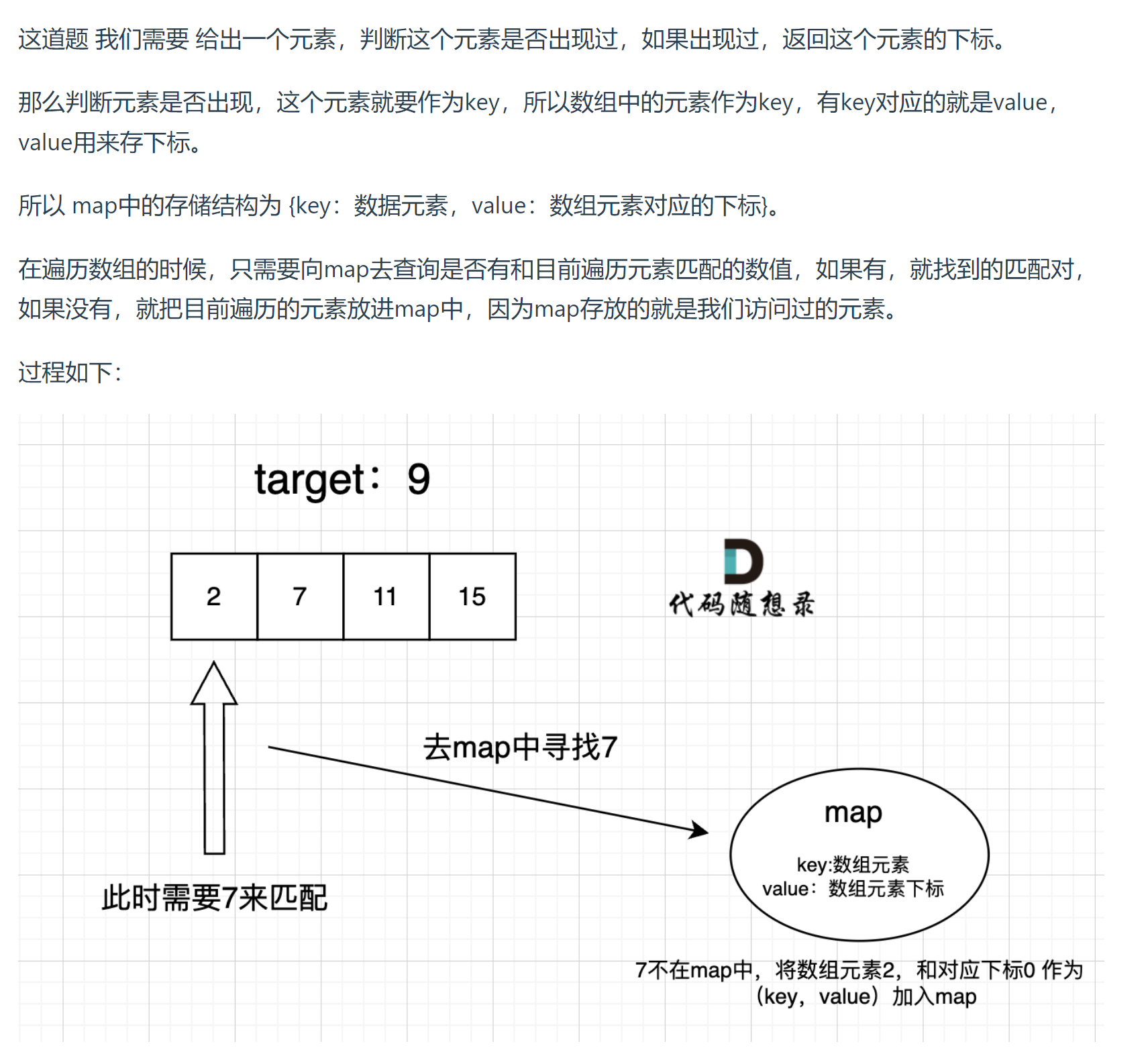
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] result = new int[2];
HashMap<Integer, Integer> numsMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
int tmp = target - nums[i];
if(numsMap.containsKey(tmp)){
result[0] = numsMap.get(tmp);
result[1] = i;
return result;
}
numsMap.put(nums[i], i);
}
return null;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
首先我在强调一下 什么时候使用哈希法,当我们需要查询一个元素是否出现过,或者一个元素是否在集合里的时候,就要第一时间想到哈希法。
# 454. 四数相加

分组,两个两个弄
class Solution {
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> abHashMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
int n = nums1.length;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
int sum = nums1[i] + nums2[j];
if(abHashMap.containsKey(sum)){
abHashMap.put(sum, abHashMap.get(sum) + 1);
}else{
abHashMap.put(sum, 1);
}
}
}
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
int toFind = - nums3[i] - nums4[j];
if(abHashMap.containsKey(toFind) && abHashMap.get(toFind) > 0){
result += abHashMap.get(toFind);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 383. 赎金信

class Solution {
public boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {
int[] tmp = new int[26];
for(int i = 0; i < magazine.length(); i++){
tmp[magazine.charAt(i) - 'a'] ++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < ransomNote.length(); i++){
if(tmp[ransomNote.charAt(i) - 'a'] == 0){
return false;
}else{
tmp[ransomNote.charAt(i) - 'a'] --;
}
}
return true;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Arrays.sort() 从小到大排序
# 15.三数之和

- 先排序数组,再使用双指针 [i, left, right]
- 去重的时候拿i和之前的i-1 比较,如果有重复的就直接跳过这组
- https://programmercarl.com/0015.%E4%B8%89%E6%95%B0%E4%B9%8B%E5%92%8C.html#%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E8%A7%A3%E6%B3%95
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
int left = 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
// 排序之后如果第一个元素已经大于零,那么无论如何组合都不可能凑成三元组,直接返回结果就可以了
if (nums[i] > 0) {
return result;
}
//去重,要是i跟上一轮一样直接跳过
if(i >= 1 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){
continue;
}
left = i + 1;
right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right){
if(nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0){
right --;
}
else if(nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < 0){
left ++;
}else{
//找到结果
List<Integer> toBeAdded = new ArrayList<Integer>();
toBeAdded.add(nums[i]);
toBeAdded.add(nums[left]);
toBeAdded.add(nums[right]);
result.add(toBeAdded);
// 在left和right遍历的时候碰到下一个值是一样的就直接跳过(去重)
while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
//只动一个指针的话不可能为0,所以要两个一起动
right--;
left++;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# 18. 四数之和
思路和三数之和差不多

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int a = 0; a < nums.length; a++){
//这边注意判断 > 0
if(nums[a] > 0 && nums[a] > target){
return result;
}
if(a >= 1 && nums[a] == nums[a - 1]){
continue;
}
for(int b = a + 1; b < nums.length; b++){
if(b > a + 1 && nums[b] == nums[b - 1]){
continue;
}
int left = b + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right){
if(nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[left] + nums[right] < target){
left ++;
}
else if(nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[left] + nums[right] > target){
right --;
}else{
//add
List<Integer> toBeAdded = new ArrayList<Integer>();
toBeAdded.add(nums[a]);
toBeAdded.add(nums[b]);
toBeAdded.add(nums[left]);
toBeAdded.add(nums[right]);
result.add(toBeAdded);
// 这里left < right 不能漏掉!!
while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]){
left ++;
}
while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]){
right --;
}
left ++;
right --;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
