Ch04 Stack And Queue
Yang Haoran 7/15/2023 StackQueue
# Java Stack
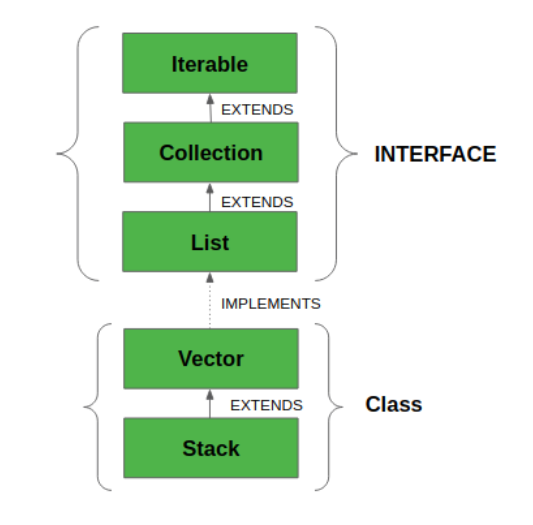
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
stack.size();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Java Queue
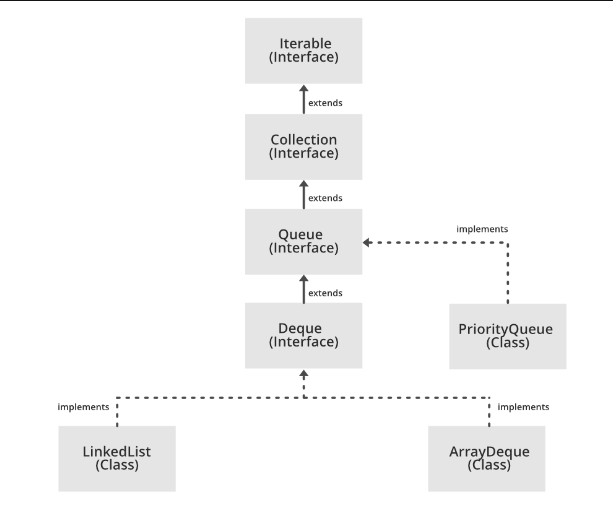
Queue可以用linkedList
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // add elements to the queue queue.add("apple"); queue.add("banana"); queue.add("cherry"); // print the queue System.out.println("Queue: " + queue); // remove the element at the front of the queue String front = queue.remove(); System.out.println("Removed element: " + front); // peek at the element at the front of the queue String peeked = queue.peek(); queue.size(); String poll = queue.poll(); //delete and return1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# Java deque
双向队列(两边都可以入栈出栈)
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.addFirst(1);
deque.addLast(2);
int first = deque.removeFirst();
int last = deque.removeLast();
// Add at the first
deque.push("Element 4 (Head)");
// Add at the last
deque.offer("Element 5 (Tail)");
deque.getFirst();
deque.getLast();
System.out.println(deque.pop());
System.out.println(deque.poll());
System.out.println(deque.pollFirst());
System.out.println(deque.pollLast());
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
在单调队列的应用上,它经常用来解决定长连续子区间的最值问题
# 232.用栈实现队列
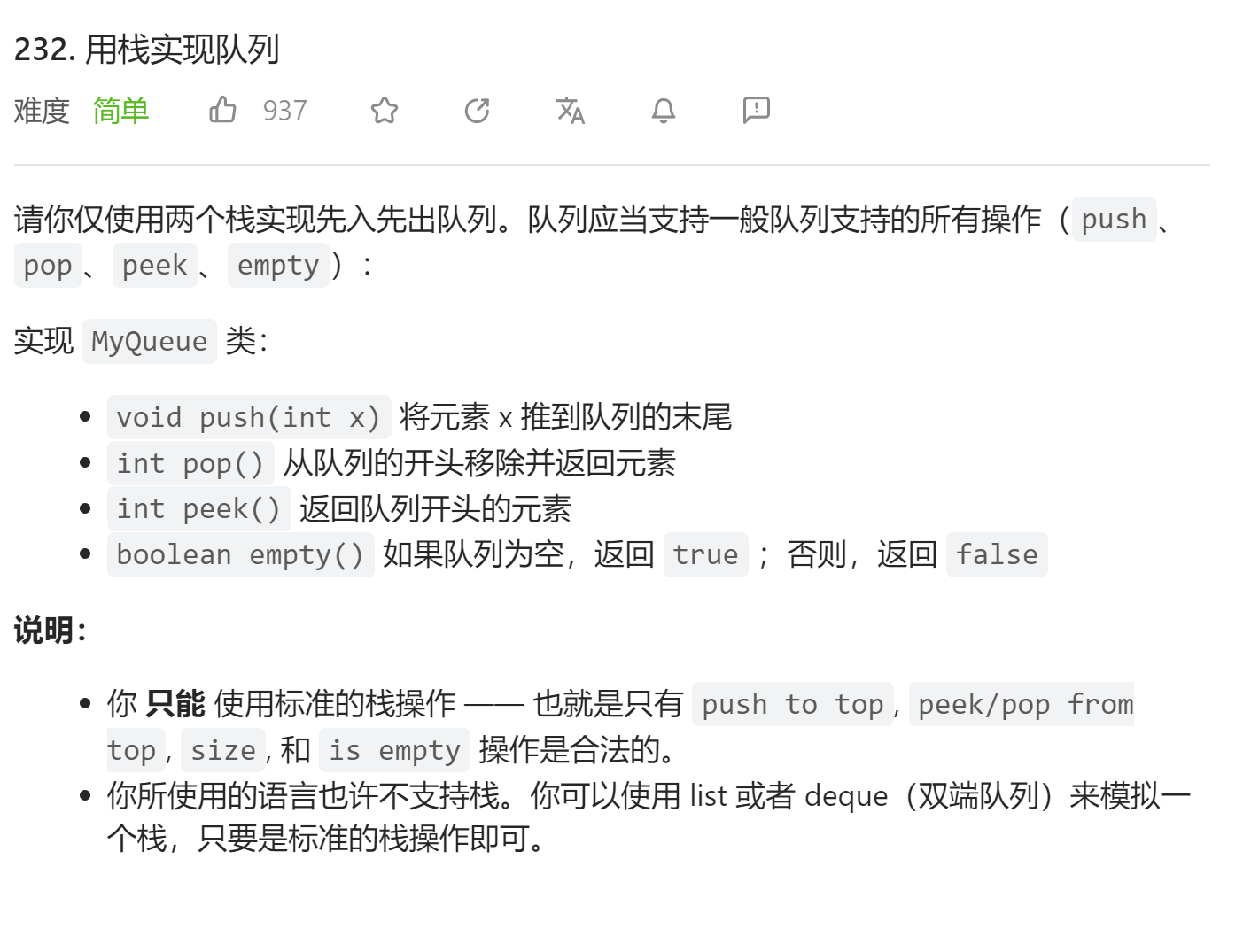
- 出栈队列只有空了才能把入栈队列元素移动过来

class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stackIn;
Stack<Integer> stackOut;
public MyQueue() {
stackIn = new Stack<Integer>();
stackOut = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stackIn.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(!stackOut.isEmpty()){
return stackOut.pop();
}
while(!stackIn.isEmpty()){
stackOut.push(stackIn.pop());
}
return stackOut.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(!stackOut.isEmpty()){
return stackOut.peek();
}
while(!stackIn.isEmpty()){
stackOut.push(stackIn.pop());
}
return stackOut.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stackOut.isEmpty() && stackIn.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
# 225. 用队列实现栈

class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue1;
Queue<Integer> queue2;
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
public void push(int x) {
queue1.offer(x);
}
public int pop() {
while(queue1.size() > 1){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
int result = queue1.poll();
while(!queue2.isEmpty()){
queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
}
return result;
}
public int top() {
while(queue1.size() > 1){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
int result = queue1.peek();
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
return result;
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56

一下代码更简单,在push的时候就搞定顺序
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue1; // 和栈中保持一样元素的队列
Queue<Integer> queue2; // 辅助队列
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
queue2.offer(x); // 先放在辅助队列中
while (!queue1.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
Queue<Integer> queueTemp;
queueTemp = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = queueTemp; // 最后交换queue1和queue2,将元素都放到queue1中
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return queue1.poll(); // 因为queue1中的元素和栈中的保持一致,所以这个和下面两个的操作只看queue1即可
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# 20. 有效的括号

class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Map<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<Character, Character>();
map.put('(', ')');
map.put(')','%');
map.put(']','%');
map.put('}','%');
map.put('[', ']');
map.put('{', '}');
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
if(stack.size() == 0){
stack.push(s.charAt(i));
continue;
}
if(map.get(stack.peek()) != s.charAt(i)){
stack.push(s.charAt(i));
}else{
stack.pop();
}
}
return stack.size() == 0;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项

- 用队列实现的话最后不用翻转
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicates(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
if(stack.isEmpty()){
stack.push(s.charAt(i));
continue;
}
if(s.charAt(i) == stack.peek()){
stack.pop();
}else{
stack.push(s.charAt(i));
}
}
char[] tmp = new char[stack.size()];
int j = 0;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
tmp[j++] = stack.pop();
}
for(int i = 0; i < tmp.length / 2; i++){
char t = tmp[i];
tmp[i] = tmp[tmp.length - 1 - i];
tmp[tmp.length - 1 - i] = t;
}
return new String(tmp);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 150. 逆波兰表达式求值
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++){
if(tokens[i].equals("+")){
stack.push(stack.pop() + stack.pop());
}else if(tokens[i].equals("-")){
int a = stack.pop();
int b = stack.pop();
stack.push(b - a);
}else if(tokens[i].equals("*")){
stack.push(stack.pop() * stack.pop());
}else if(tokens[i].equals("/")){
int a = stack.pop();
int b = stack.pop();
stack.push(b / a);
}else{
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(tokens[i]));
}
}
return stack.peek();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 239. 滑动窗口最大值
- 永远保持最新鲜的最大值(至多两个),单调队列


class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int[] result = new int[nums.length - k + 1];
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
for(int j = 0; j < k; j++){
add(deque, nums[j]);
}
result[0] = deque.getFirst();
int m = 1;
for(int i = k; i < nums.length; i++){
remove(deque, nums[i - k]);
add(deque, nums[i]);
result[m++] = deque.getFirst();
}
return result;
}
public void add(Deque<Integer> deque, int i){
while(deque.size() > 0 && i > deque.getLast()){
deque.removeLast();
}
deque.addLast(i);
}
public void remove(Deque<Integer> deque, int i){
if(i == deque.getFirst()){
deque.removeFirst();
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 347.前 K 个高频元素

- 暴力法
class Solution {
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(map.containsKey(nums[i])){
map.put(nums[i], map.get(nums[i]) + 1);
}else{
map.put(nums[i], 1);
}
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> tmp = new Stack<>();
for(int key: map.keySet()){
while(stack.size() != 0 && map.get(stack.peek()) > map.get(key)){
tmp.push(stack.pop());
}
stack.push(key);
while(tmp.size() > 0){
stack.push(tmp.pop());
}
}
int[] result = new int[k];
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
result[i] = stack.pop();
}
return result;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31


- PriorityQueue会在add的时候自动排序


//解法1:基于大顶堆实现
public int[] topKFrequent1(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();//key为数组元素值,val为对应出现次数
for(int num:nums){
map.put(num,map.getOrDefault(num,0)+1);
}
//在优先队列中存储二元组(num,cnt),cnt表示元素值num在数组中的出现次数
//出现次数按从队头到队尾的顺序是从大到小排,出现次数最多的在队头(相当于大顶堆)
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((pair1, pair2)->pair2[1]-pair1[1]);
for(Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> entry:map.entrySet()){//大顶堆需要对所有元素进行排序
pq.add(new int[]{entry.getKey(),entry.getValue()});
}
int[] ans = new int[k];
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){//依次从队头弹出k个,就是出现频率前k高的元素
ans[i] = pq.poll()[0];
}
return ans;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# lamda表达式用法