Ch06 Recall
Yang Haoran 7/26/2023 BinaryTree
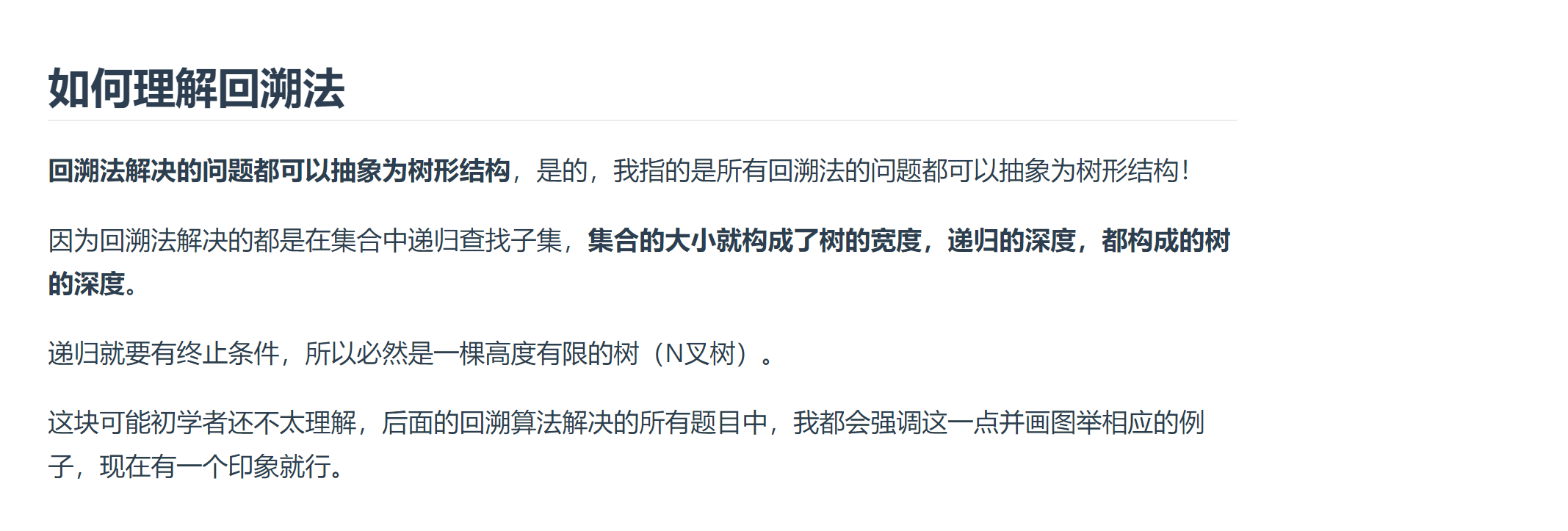
# Recall
- 递归函数下面的就叫回溯


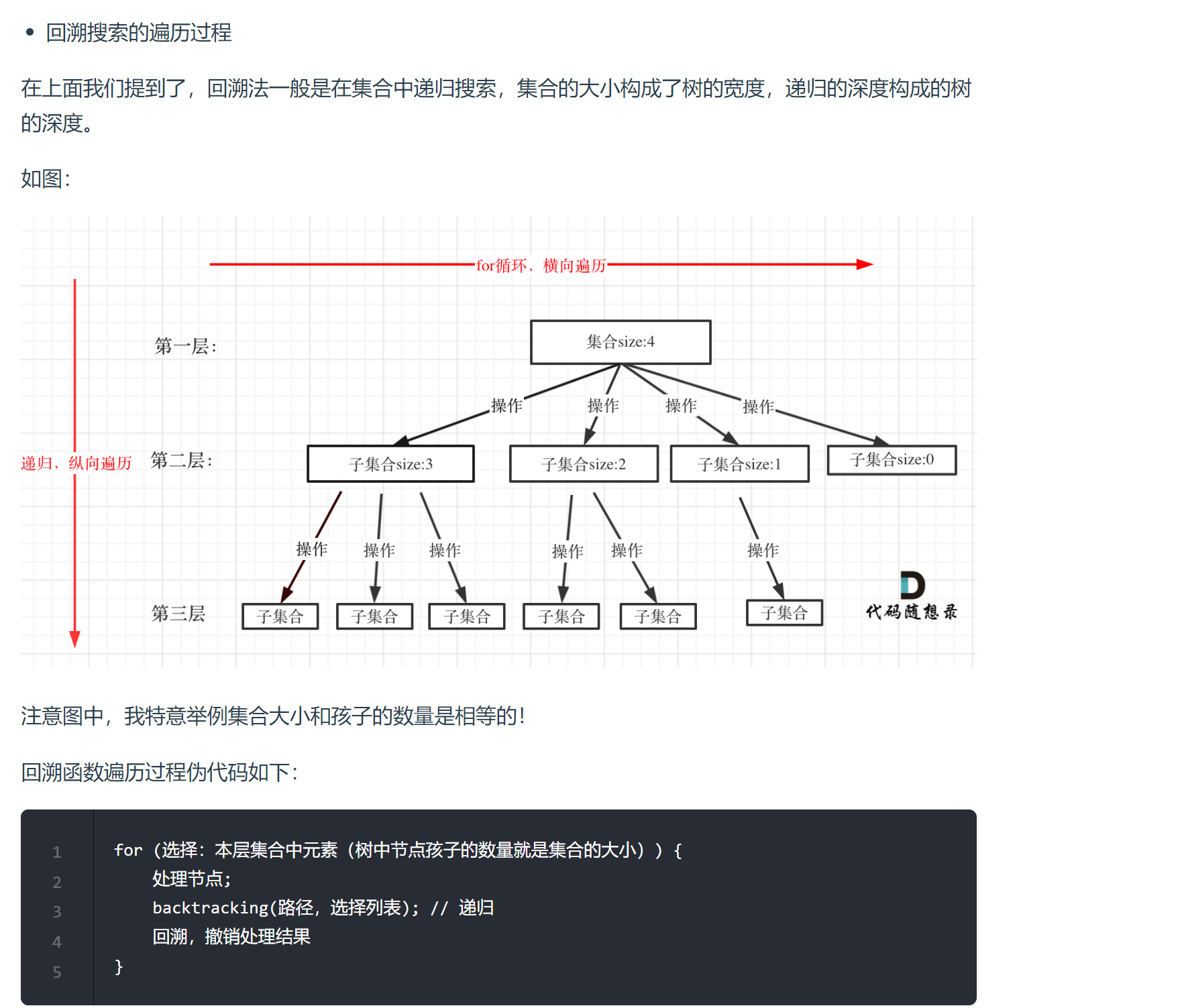

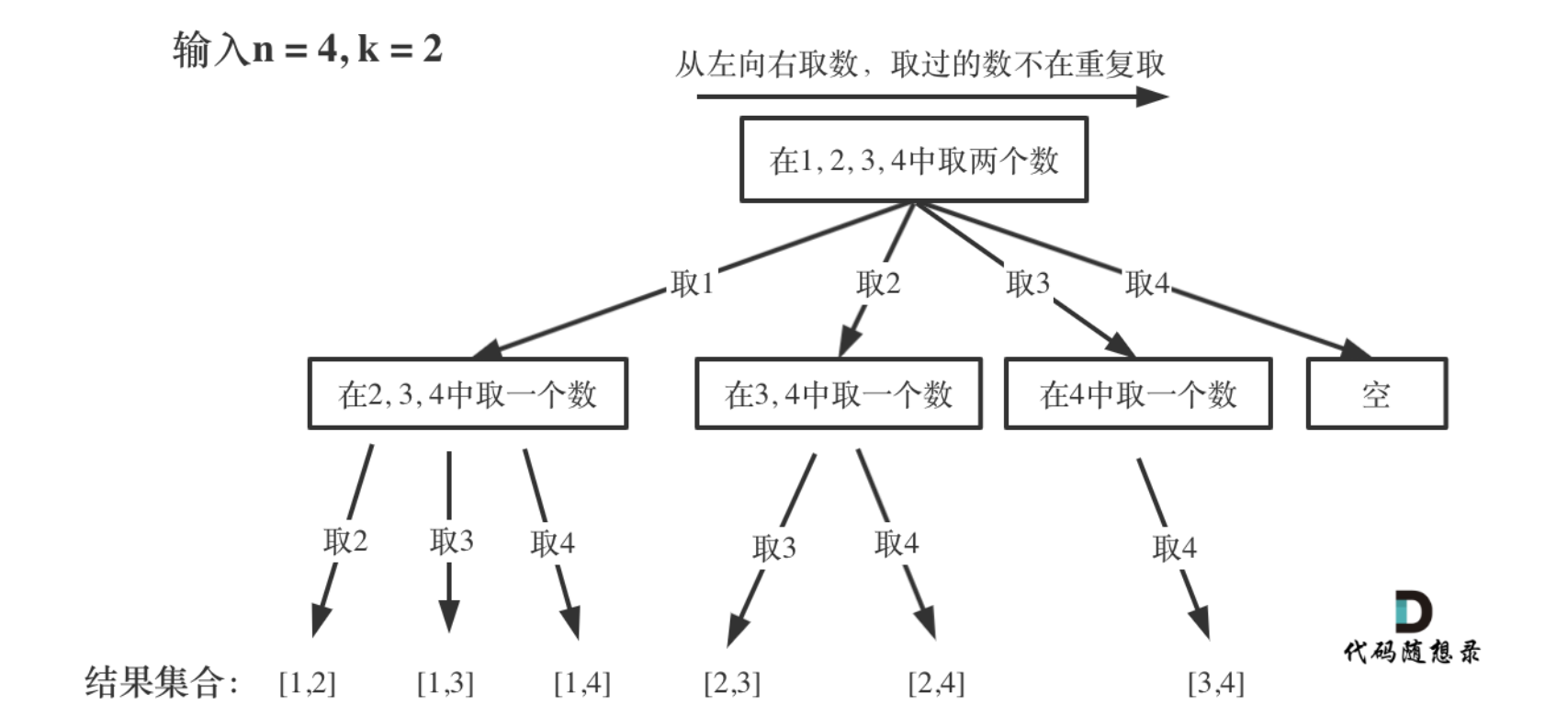
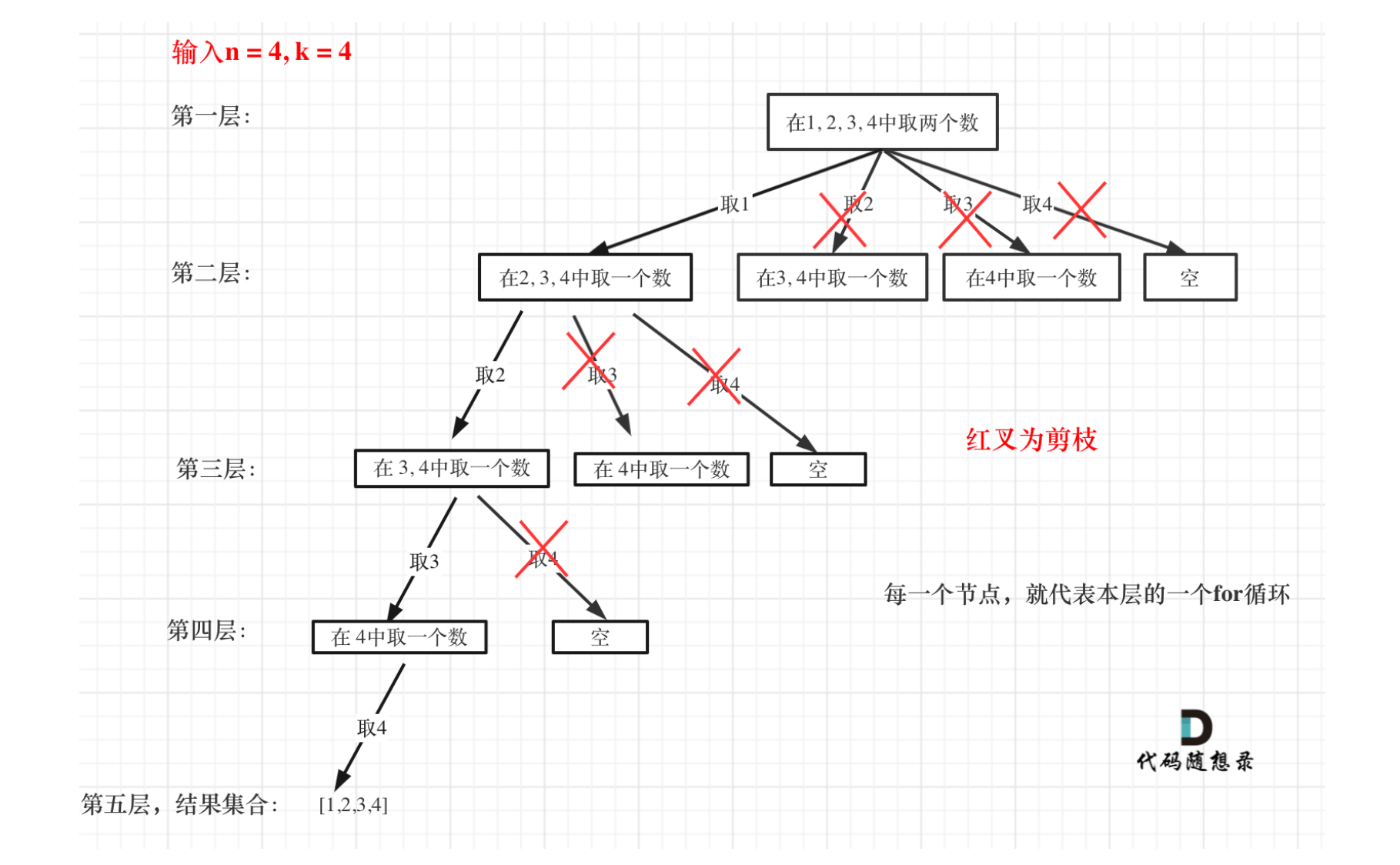
# 77. 组合 (opens new window)

优化

class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
backtrace(n, k, 1);
return result;
}
void backtrace(int n, int k, int startIndex){
if(path.size() == k){
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++){
//优化剪枝: for(int i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1; i++){
path.add(i);
backtrace(n, k, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 216. 组合总和 III (opens new window)

class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
backtrace(k, n, 1);
return result;
}
void backtrace(int k, int n, int start){
if(path.size() == k && sum == n){
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < 10; i++){
path.add(i);
sum = sum + i;
backtrace(k, n, i + 1);
sum = sum - path.get(path.size() - 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
- 也可以通过sum剪枝,也可以通过元素个数剪枝
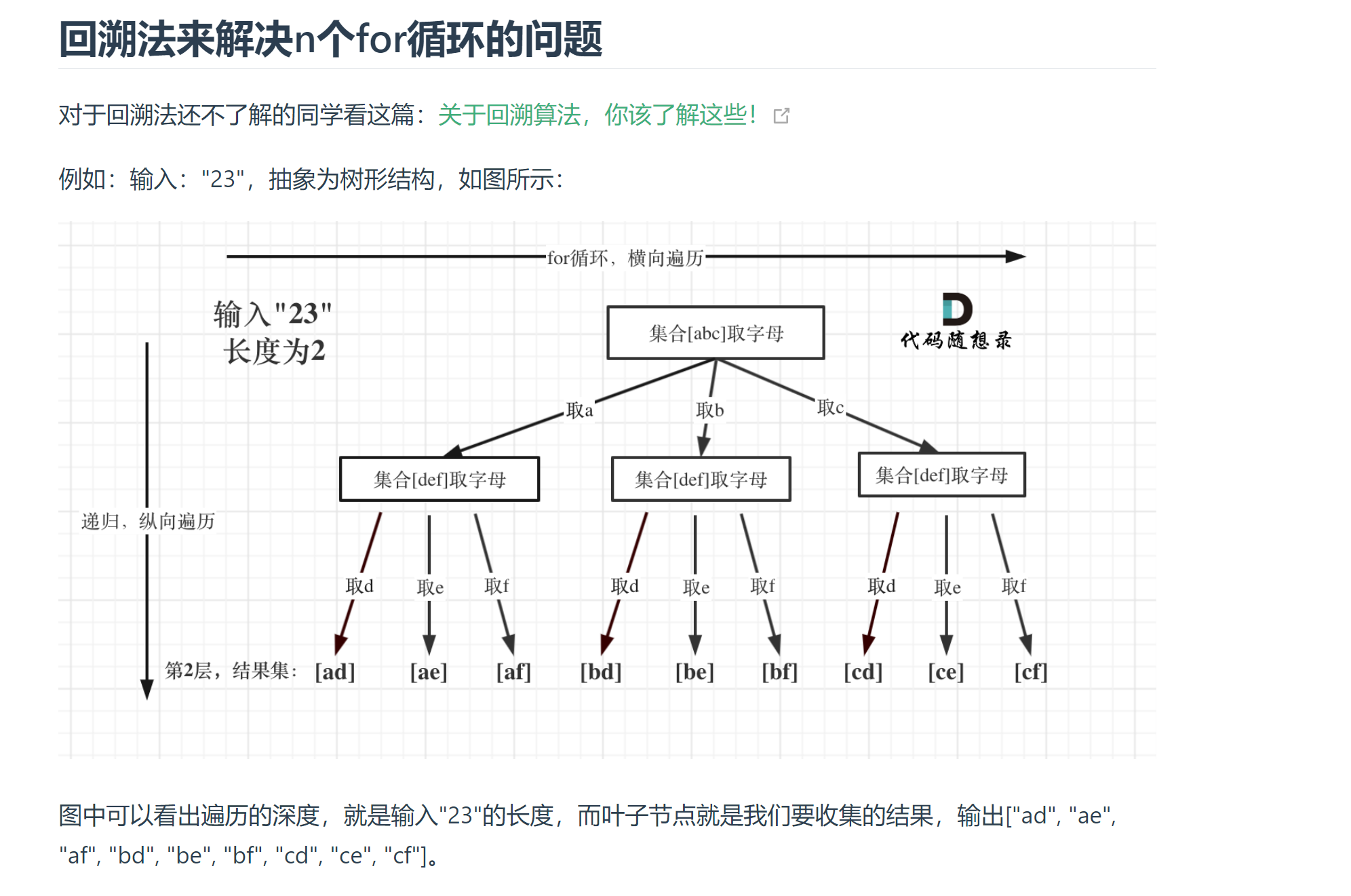
# 17. 电话号码的字母组合 (opens new window)
class Solution {
String[] map = new String[]{"", "", "abc", "def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"};
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Character> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
if(digits.length() == 0){
return result;
}
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < digits.length(); i++){
list.add(map[digits.charAt(i) - '0']);
}
backtrace(list, 0);
return result;
}
//i:迭代到第几个字符串
void backtrace(List<String> list, int i){
//收获结果
if(path.size() == list.size()){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int j = 0; j < path.size(); j++){
sb.append(path.get(j));
}
result.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
for(int j = 0; j < list.get(i).length(); j++){
path.add(list.get(i).charAt(j));
backtrace(list, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# 39. 组合总和 (opens new window)
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
backtrace(candidates, 0, target);
return result;
}
void backtrace(int[] candidates, int startIndex, int target){
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum < target; i++){
path.add(candidates[i]);
sum = sum + candidates[i];
backtrace(candidates, i, target);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
sum = sum - candidates[i];
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 40. 组合总和 II (opens new window)
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0;
int pre = -1;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtrace(candidates, 0, target);
return result;
}
void backtrace(int[] candidates, int startIndex, int target){
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum < target; i++){
if(candidates[i] == pre){
continue;
}
path.add(candidates[i]);
sum = sum + candidates[i];
backtrace(candidates, i + 1, target);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
sum = sum - candidates[i];
pre = candidates[i];
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 131. 分割回文串 (opens new window)
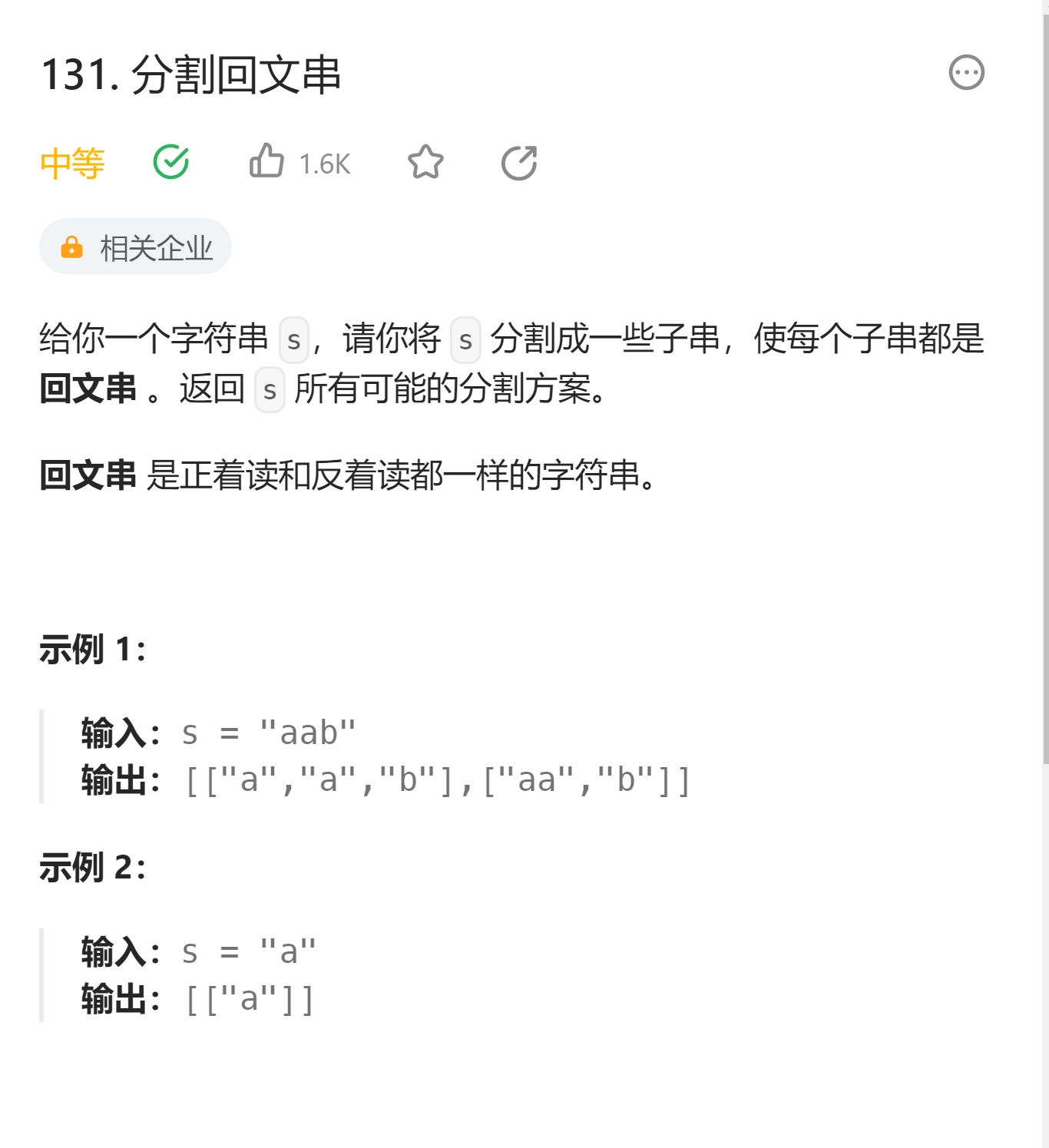
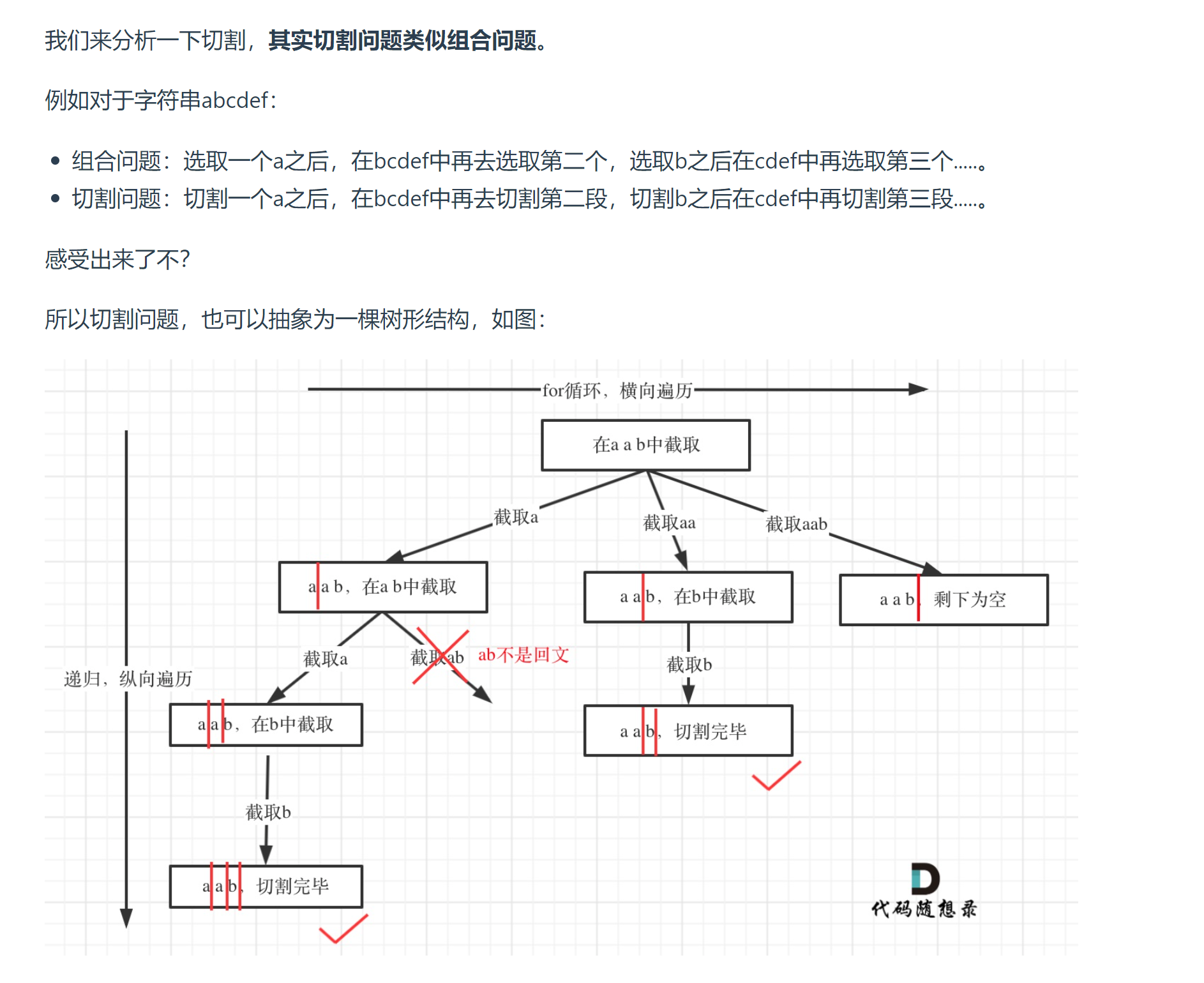
class Solution {
List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backtrace(s, 0);
return result;
}
public void backtrace(String s, int startIndex){
if(startIndex == s.length()){
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++){
String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
//如果左边是的话
if(isReverse(str)){
path.add(str);
backtrace(s, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
boolean isReverse(String s){
for(int i = 0; i < s.length() / 2; i++){
if(s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(s.length() - i - 1)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 93. 复原 IP 地址 (opens new window)
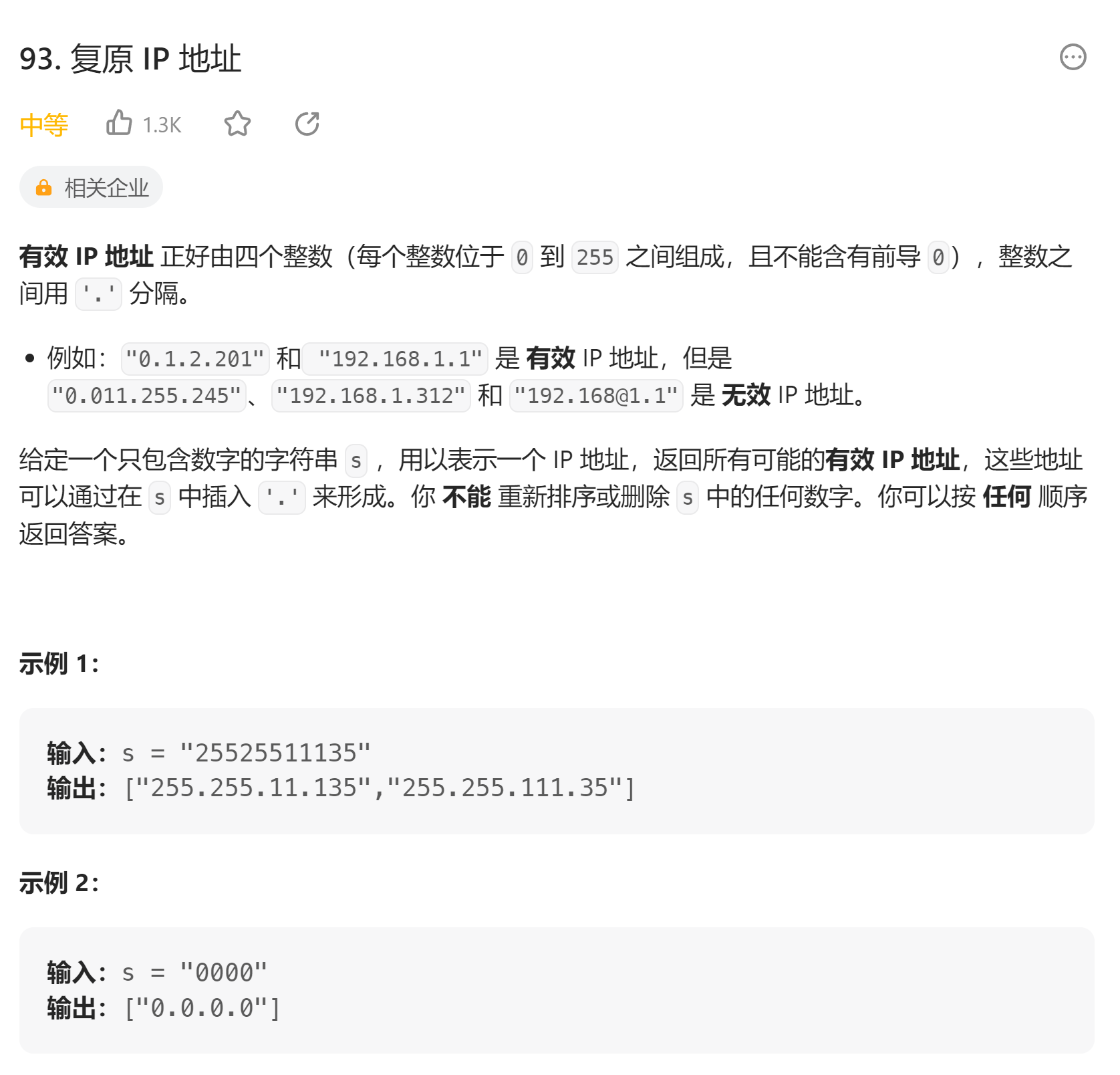
- 自己全部判断的方法,耗时长
class Solution {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
backtrace(s, 0);
return result;
}
void backtrace(String s, int startIndex){
if(path.size() > 4) return;
if(startIndex >= s.length() && path.size() == 4){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(String str: path){
sb.append(str + ".");
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
result.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++){
String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
if(isVaild(str)){
path.add(str);
backtrace(s, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
boolean isVaild(String s){
if(s.length() >= 4) return false;
int value = Integer.valueOf(s);
if(s.equals("0")){
return true;
}
if(s.charAt(0) != '0' && value <= 255 && value > 0){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# 78. 子集 (opens new window)
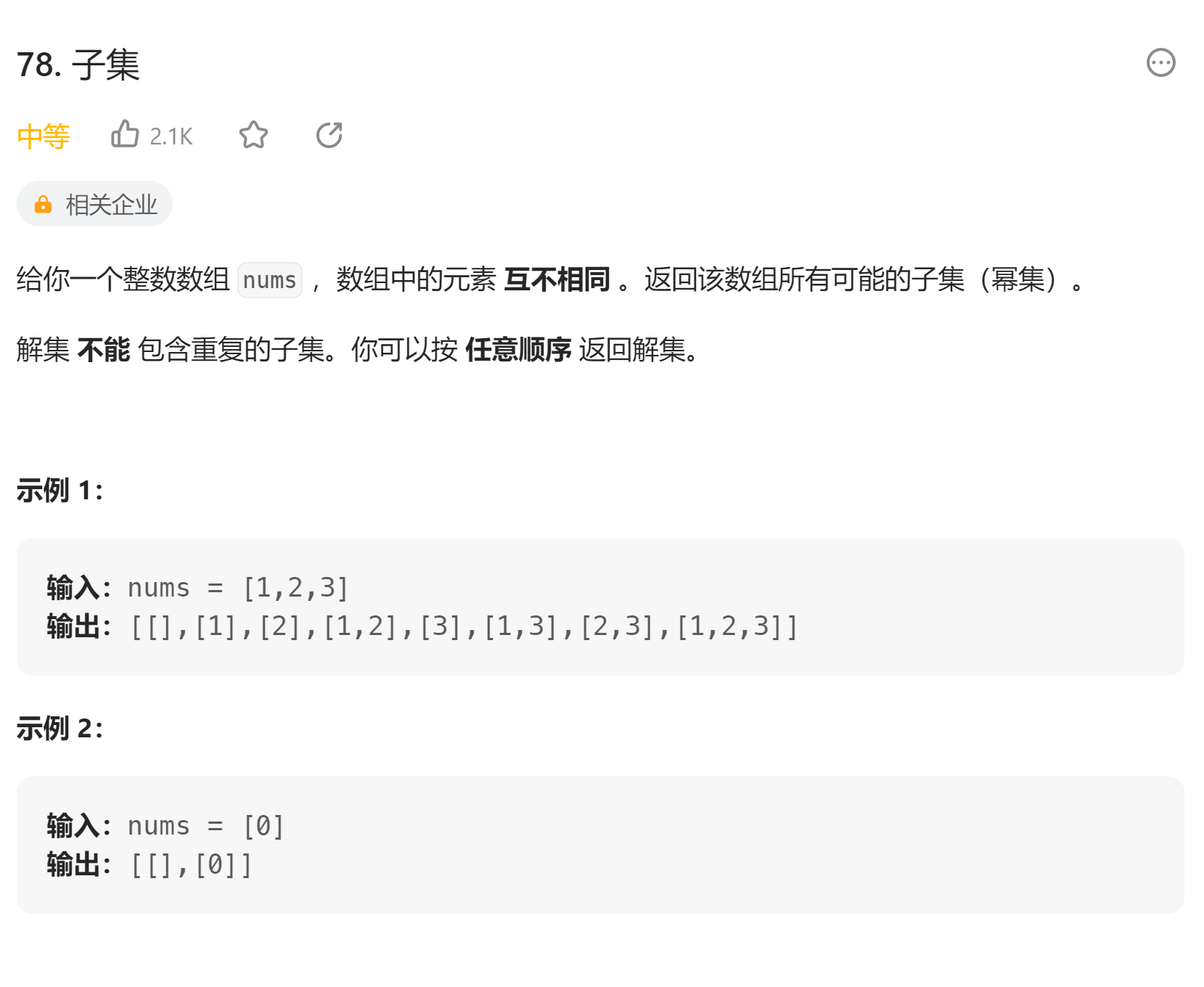
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
backtrace(nums, 0);
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
return result;
}
void backtrace(int[] nums, int startIndex){
// if(startIndex >= nums.length){
// return;
// }
for(int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){
path.add(nums[i]);
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
backtrace(nums, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 90. 子集 II (opens new window)
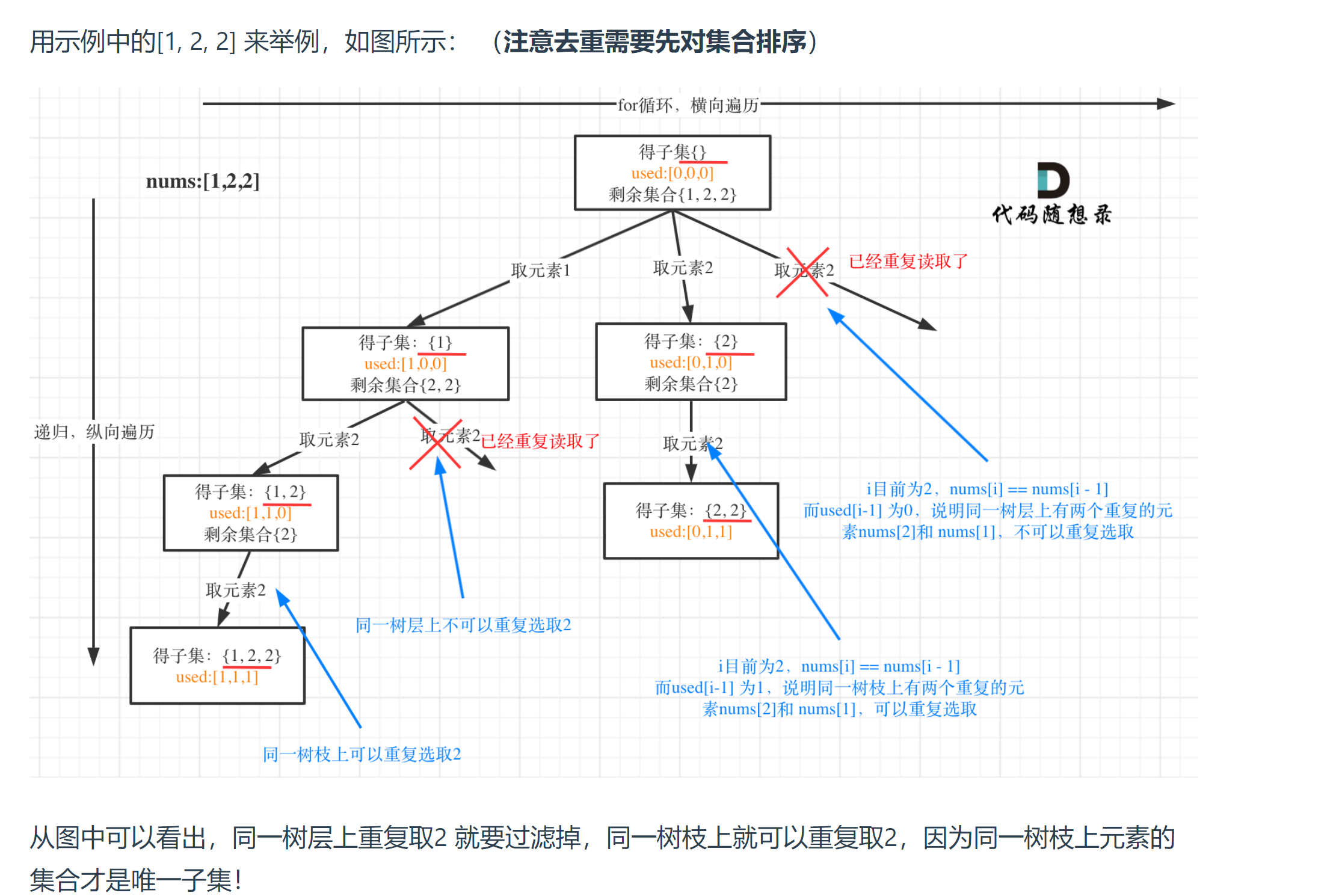
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtrace(nums, 0);
result.add(new ArrayList());
return result;
}
void backtrace(int[] nums, int startIndex){
for(int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){
//注意这边是startIndex
if(i > startIndex && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
backtrace(nums, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 491. 递增子序列 (opens new window)

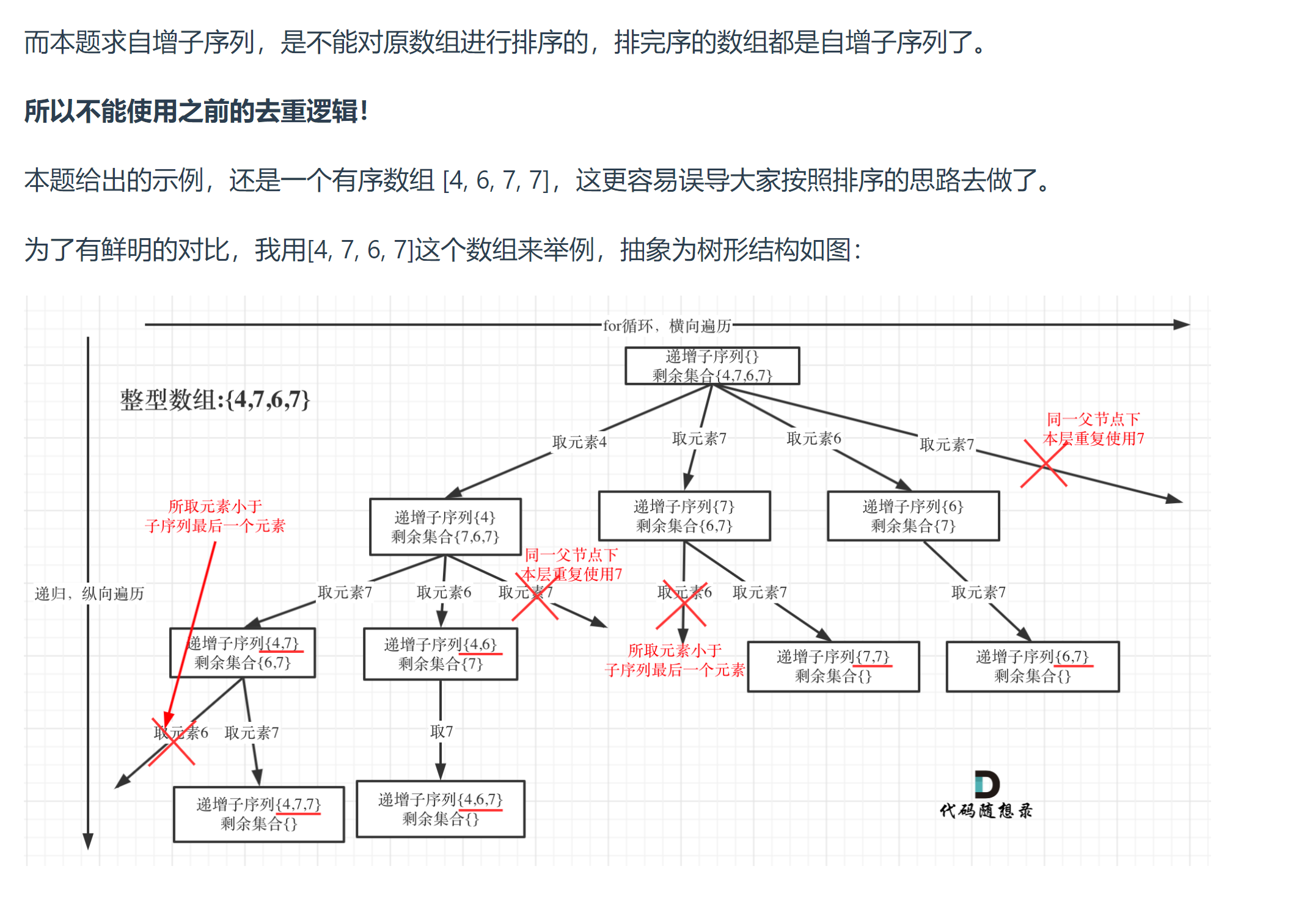
- 注意:与同一层有相同数值的节点,则跳过
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
backtrace(nums, 0);
return result;
}
void backtrace(int[] nums, int startIndex){
LOOP: for(int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){
//与同一层有相同节点则跳过
for(int j = startIndex; j < i; j++){
if(nums[j] == nums[i]) continue LOOP;
}
if(path.size() == 0 || (path.size() > 0 && nums[i] >= path.get(path.size() - 1))){
path.add(nums[i]);
if(path.size() >= 2){
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
}
backtrace(nums, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
- 当然也可以用hashset来判断
# 46. 全排列 (opens new window)
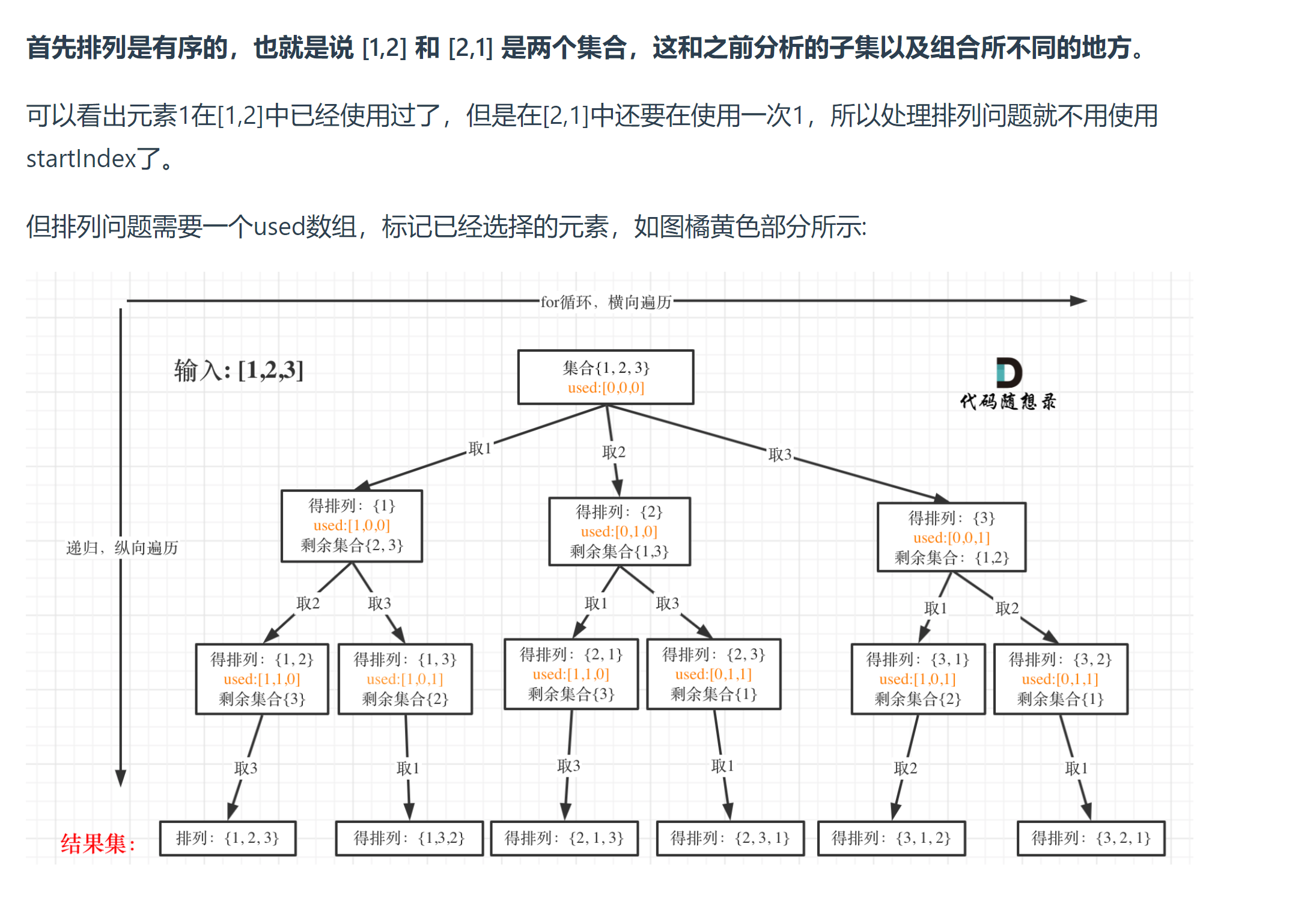
- 注意必须用used数组来判断是否使用过,递归中没startIndex,都是从头开始,并且跳过已经用过的元素
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] isUsed = new boolean[1];
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
isUsed = new boolean[nums.length];
backtrace(nums);
return result;
}
void backtrace(int[] nums){
if(path.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(isUsed[i] == false){
path.add(nums[i]);
isUsed[i] = true;
backtrace(nums);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
isUsed[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 47. 全排列 II (opens new window)
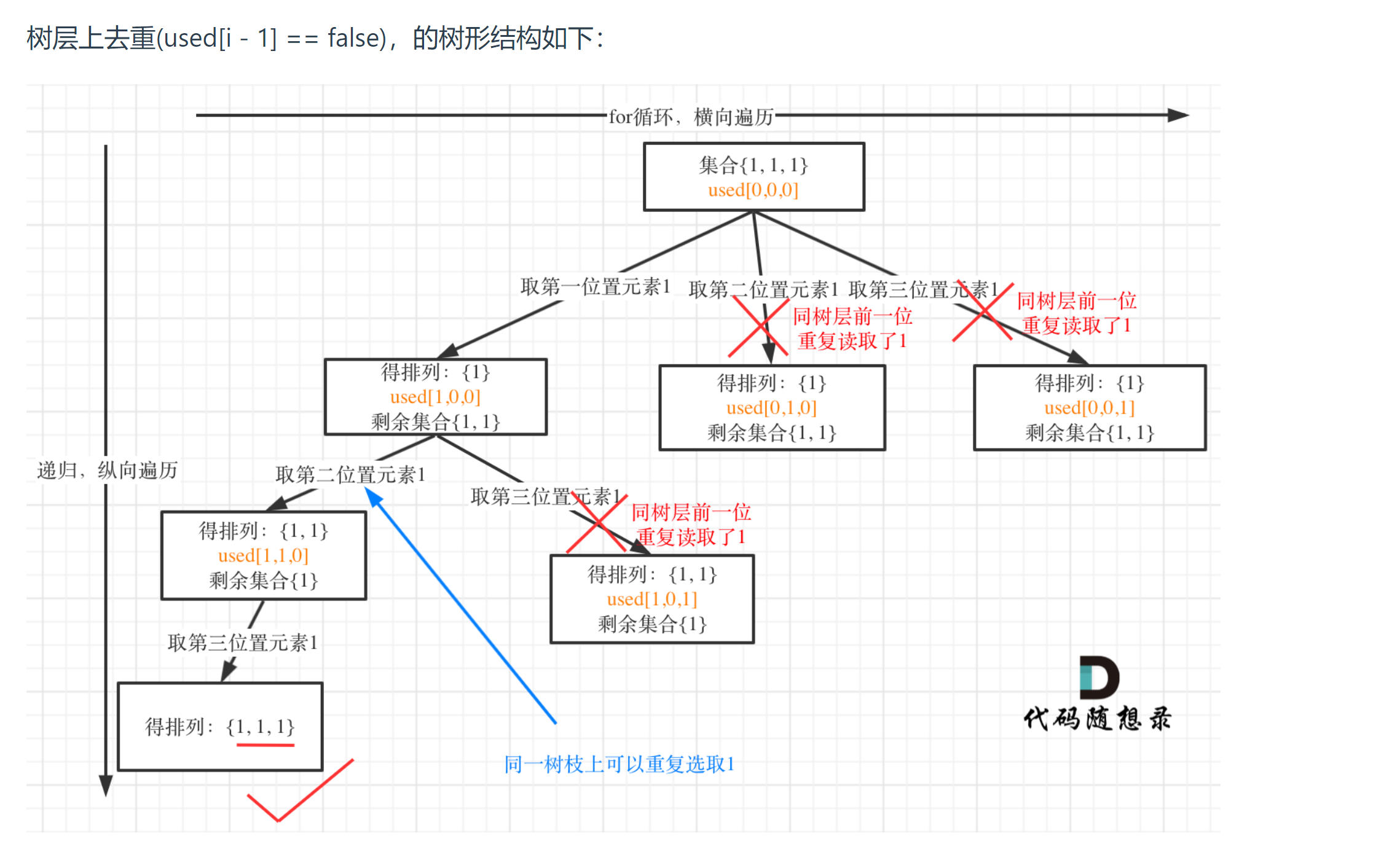
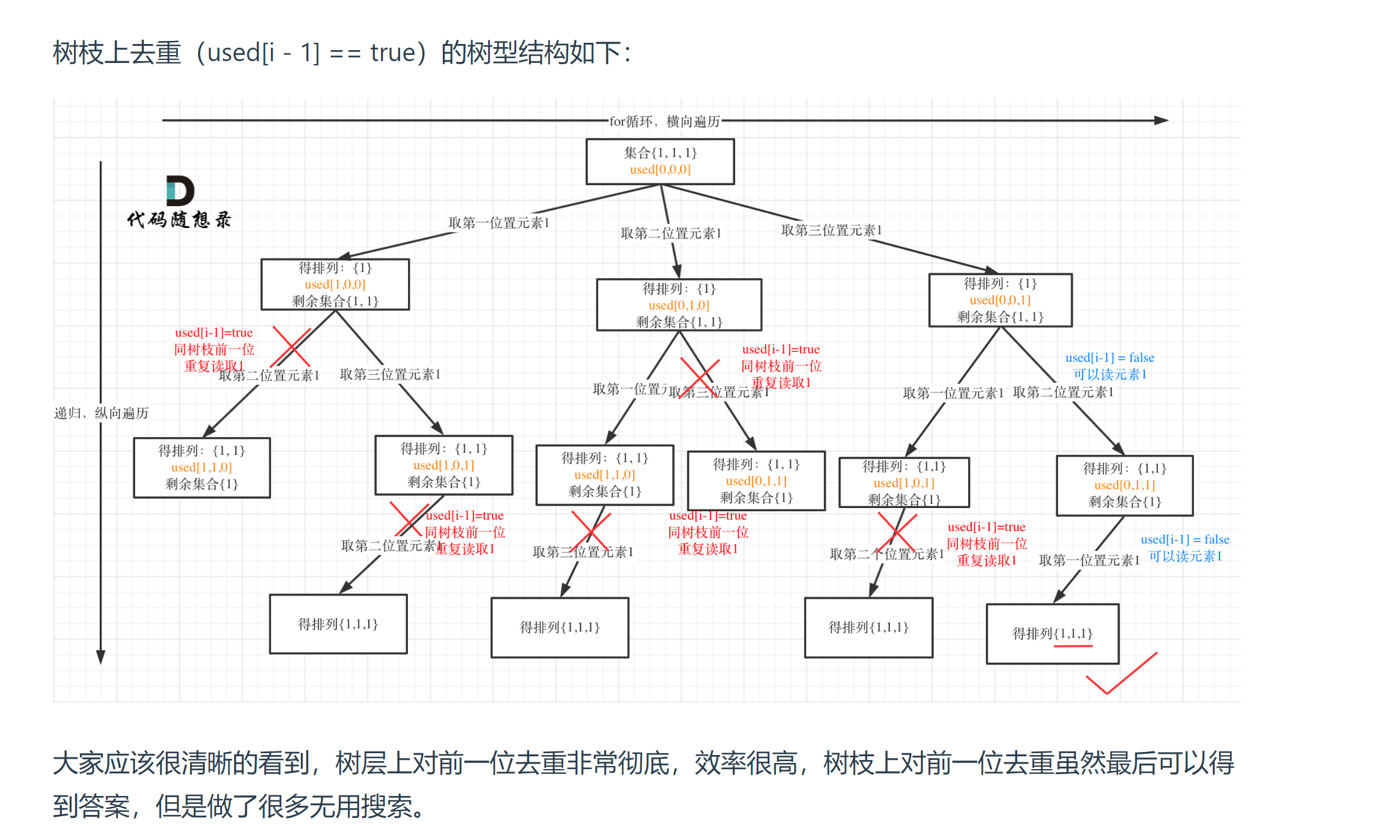
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] isUsed;
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
isUsed = new boolean[nums.length];
backtrace(nums);
return result;
}
void backtrace(int[]nums){
if(path.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
//树层去重, false的意思是前一个节点的情况已经处理完了
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && isUsed[i - 1] == false){
continue;
}
if(isUsed[i] == false){
path.add(nums[i]);
isUsed[i] = true;
backtrace(nums);
isUsed[i] = false;
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 332. 重新安排行程 (opens new window)
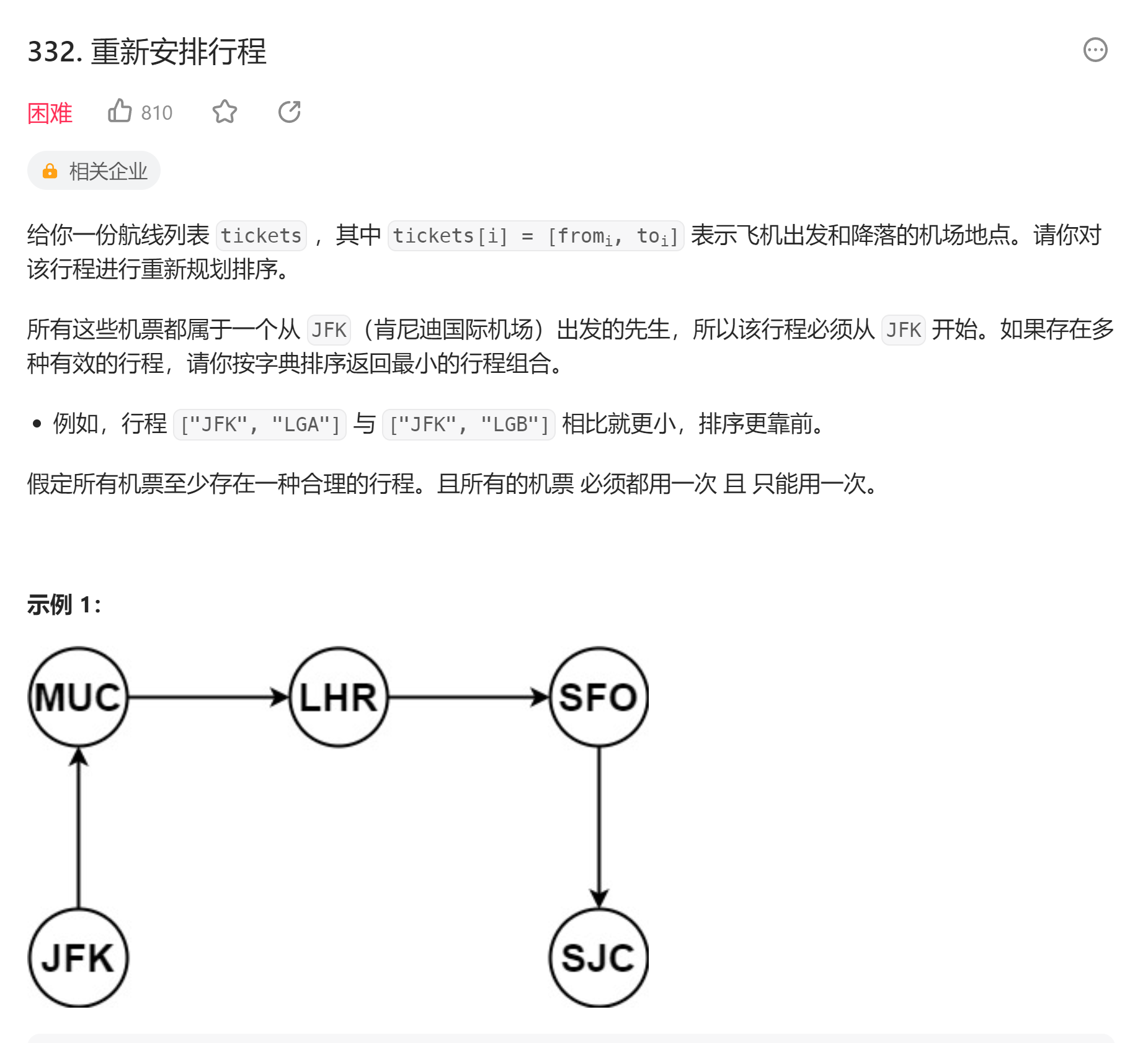
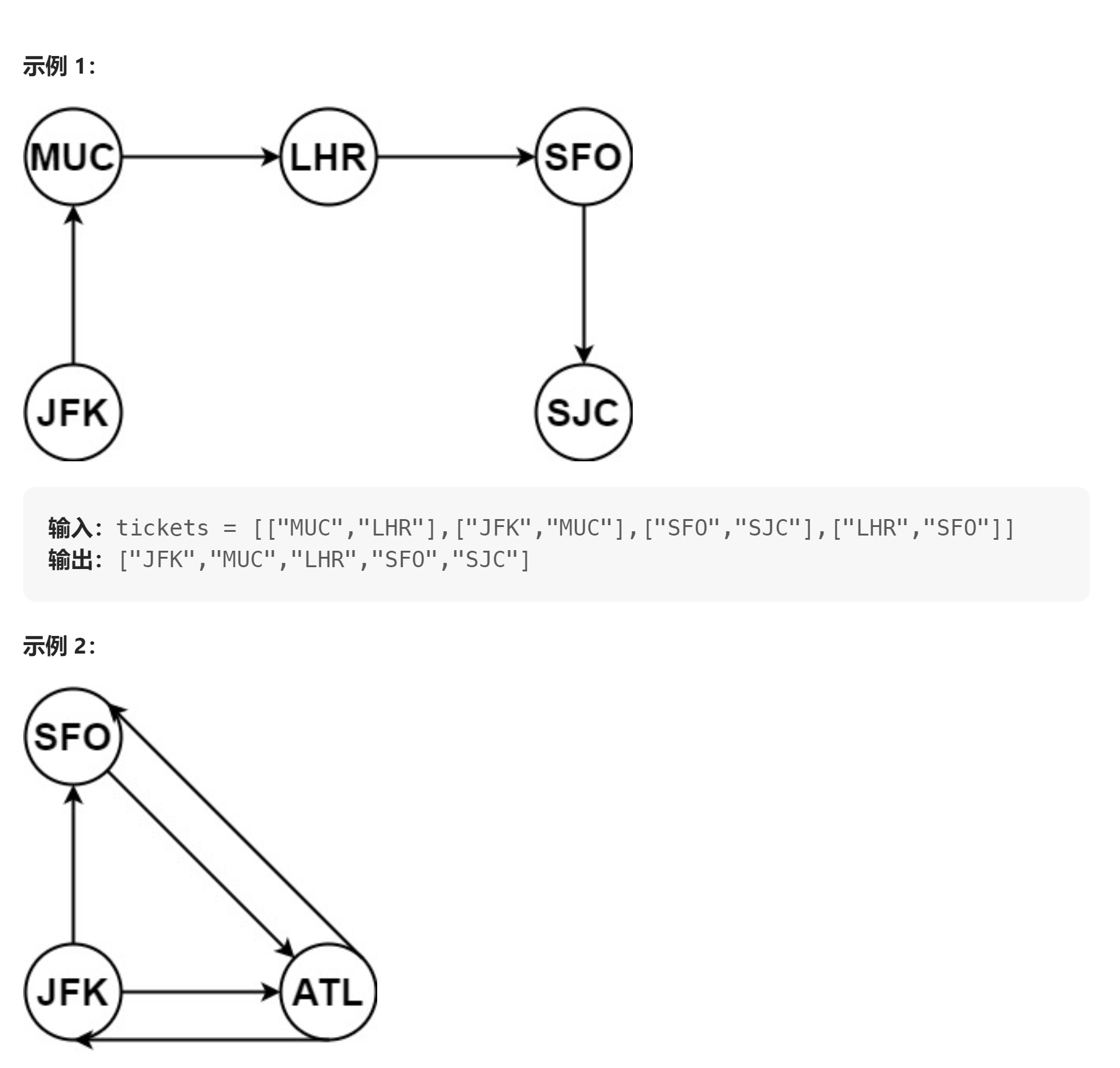
- 自己想的
class Solution {
HashMap<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0;
public List<String> findItinerary(List<List<String>> tickets) {
for(List<String> list: tickets){
// sum++;
if(!map.containsKey(list.get(0))){
List<String> addList = new ArrayList<>();
addList.add(list.get(1));
map.put(list.get(0), addList);
}else{
map.get(list.get(0)).add(list.get(1));
Collections.sort(map.get(list.get(0)));
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry: map.entrySet() ) {
System.out.println("------");
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
for(String s: entry.getValue()){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
result.add("JFK");
backtrace(tickets.size());
return result;
// return null;
}
boolean backtrace(int len){
if(sum == len){
return true;
}
List<String> list = map.get(result.get(result.size() - 1));
if(list == null || list.size() == 0) return false;
// if() return true;
//根据上一程的终点遍历
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
String start = result.get(result.size() - 1);
String end = list.get(i);
delete(start, end);
result.add(end);
sum++;
if(backtrace(len)){
return true;
}
sum--;
result.remove(result.size() - 1);
add(start, end);
}
return false;
}
//通过起点搜索到机票的合集
List<String> search(String start){
return map.get(start);
}
// 删除用过的机票
void delete(String start, String end){
List<String> list = map.get(start);
for(String s: list){
if(s.equals(end)){
list.remove(end);
return;
}
}
}
//把机票加回来
void add(String start, String end){
List<String> list = map.get(start);
list.add(end);
Collections.sort(list);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
优化

class Solution {
private Deque<String> res;
private Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> map;
private boolean backTracking(int ticketNum){
if(res.size() == ticketNum + 1){
return true;
}
String last = res.getLast();
if(map.containsKey(last)){//防止出现null
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> target : map.get(last).entrySet()){
int count = target.getValue();
if(count > 0){
res.add(target.getKey());
target.setValue(count - 1);
if(backTracking(ticketNum)) return true;
res.removeLast();
target.setValue(count);
}
}
}
return false;
}
public List<String> findItinerary(List<List<String>> tickets) {
map = new HashMap<String, Map<String, Integer>>();
res = new LinkedList<>();
for(List<String> t : tickets){
Map<String, Integer> temp;
if(map.containsKey(t.get(0))){
temp = map.get(t.get(0));
temp.put(t.get(1), temp.getOrDefault(t.get(1), 0) + 1);
}else{
temp = new TreeMap<>();//升序Map
temp.put(t.get(1), 1);
}
map.put(t.get(0), temp);
}
res.add("JFK");
backTracking(tickets.size());
return new ArrayList<>(res);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# 51. N 皇后 (opens new window)


class Solution {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
char[][] chessboard = new char[n][n];
for (char[] c : chessboard) {
Arrays.fill(c, '.');
}
backTrack(n, 0, chessboard);
return res;
}
public void backTrack(int n, int row, char[][] chessboard) {
if (row == n) {
res.add(Array2List(chessboard));
return;
}
for (int col = 0;col < n; ++col) {
if (isValid (row, col, n, chessboard)) {
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q';
backTrack(n, row+1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
public List Array2List(char[][] chessboard) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] c : chessboard) {
list.add(String.copyValueOf(c));
}
return list;
}
//只用往上边的棋盘判断,因为从上往下填充
public boolean isValid(int row, int col, int n, char[][] chessboard) {
// 检查列
for (int i=0; i<row; ++i) { // 相当于剪枝
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查45度对角线
for (int i=row-1, j=col-1; i>=0 && j>=0; i--, j--) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查135度对角线
for (int i=row-1, j=col+1; i>=0 && j<=n-1; i--, j++) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
# 37. 解数独 (opens new window)

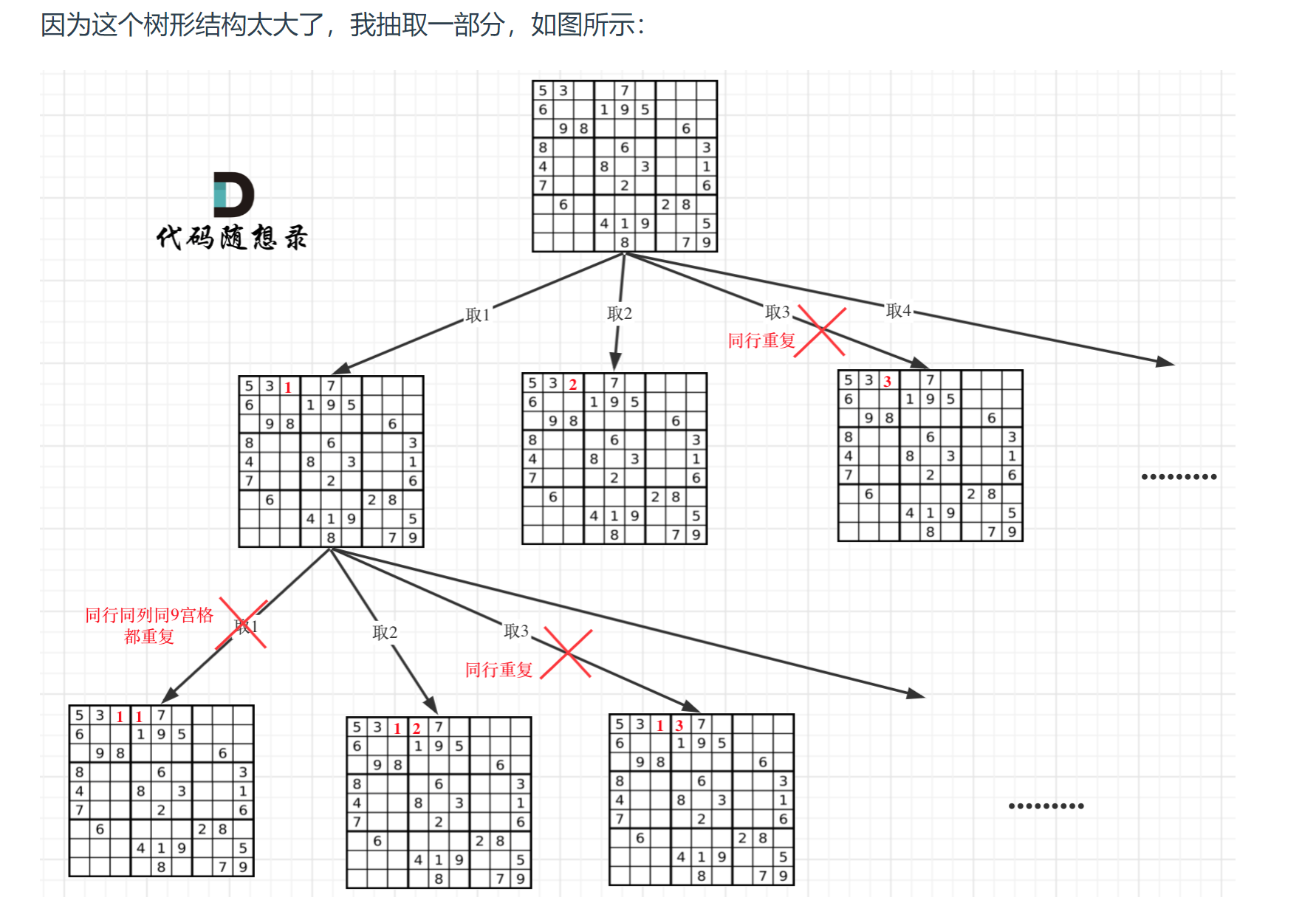
class Solution {
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
solveSudokuHelper(board);
}
private boolean solveSudokuHelper(char[][] board){
//「一个for循环遍历棋盘的行,一个for循环遍历棋盘的列,
// 一行一列确定下来之后,递归遍历这个位置放9个数字的可能性!」
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){ // 遍历行
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++){ // 遍历列
if (board[i][j] != '.'){ // 跳过原始数字
continue;
}
for (char k = '1'; k <= '9'; k++){ // (i, j) 这个位置放k是否合适
if (isValidSudoku(i, j, k, board)){
board[i][j] = k;
if (solveSudokuHelper(board)){ // 如果找到合适一组立刻返回
return true;
}
board[i][j] = '.';
}
}
// 9个数都试完了,都不行,那么就返回false
return false;
// 因为如果一行一列确定下来了,这里尝试了9个数都不行,说明这个棋盘找不到解决数独问题的解!
// 那么会直接返回, 「这也就是为什么没有终止条件也不会永远填不满棋盘而无限递归下去!」
}
}
// 遍历完没有返回false,说明找到了合适棋盘位置了
return true;
}
/**
* 判断棋盘是否合法有如下三个维度:
* 同行是否重复
* 同列是否重复
* 9宫格里是否重复
*/
private boolean isValidSudoku(int row, int col, char val, char[][] board){
// 同行是否重复
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){
if (board[row][i] == val){
return false;
}
}
// 同列是否重复
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++){
if (board[j][col] == val){
return false;
}
}
// 9宫格里是否重复
int startRow = (row / 3) * 3;
int startCol = (col / 3) * 3;
for (int i = startRow; i < startRow + 3; i++){
for (int j = startCol; j < startCol + 3; j++){
if (board[i][j] == val){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
