Ch09 Monotonic stack
Yang Haoran 8/21/2023 Stack
# 单调栈
# 739. 每日温度 (opens new window)

- 思路:https://programmercarl.com/0739.%E6%AF%8F%E6%97%A5%E6%B8%A9%E5%BA%A6.html#%E6%80%9D%E8%B7%AF
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int[] result = new int[temperatures.length];
//store the index
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(0);
for(int i = 1; i < temperatures.length; i++){
while(!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[stack.peek()] < temperatures[i]){
int a = stack.pop();
result[a] = i - a;
}
stack.push(i);
}
return result;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 496. 下一个更大元素 I (opens new window)

- 暴力,耗时也少
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int[] result = new int[nums1.length];
for(int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++){
map.put(nums2[i], i);
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++){
int value = nums1[i];
for(int j = map.get(nums1[i]) + 1; j < nums2.length; j++){
if(nums2[j] > value){
result[i] = nums2[j];
break;
}
}
if(result[i] == 0) result[i] = -1;
}
return result;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
- 单调栈,和上一题思路差不多, 注意代码中map存的num1还是num2
- stack存的是index
// 版本2
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
map.put(nums1[i], i);
}
int[] res = new int[nums1.length];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Arrays.fill(res, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums2[stack.peek()] < nums2[i]) {
int pre = nums2[stack.pop()];
if (map.containsKey(pre)) {
res[map.get(pre)] = nums2[i];
}
}
stack.push(i);
}
return res;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 503. 下一个更大元素 II (opens new window)

- 可以遍历2倍长度,优化可以用%
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int[] result = new int[nums.length];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Arrays.fill(result, -1);
for(int i = 0; i < 2 * nums.length - 1; i++){
int tmp = i;
if(tmp > nums.length - 1) tmp = tmp - nums.length;
while(!stack.isEmpty() && nums[stack.peek()] < nums[tmp]){
int index = stack.pop();
result[index] = nums[tmp];
}
stack.push(tmp);
}
return result;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 42. 接雨水 (opens new window)
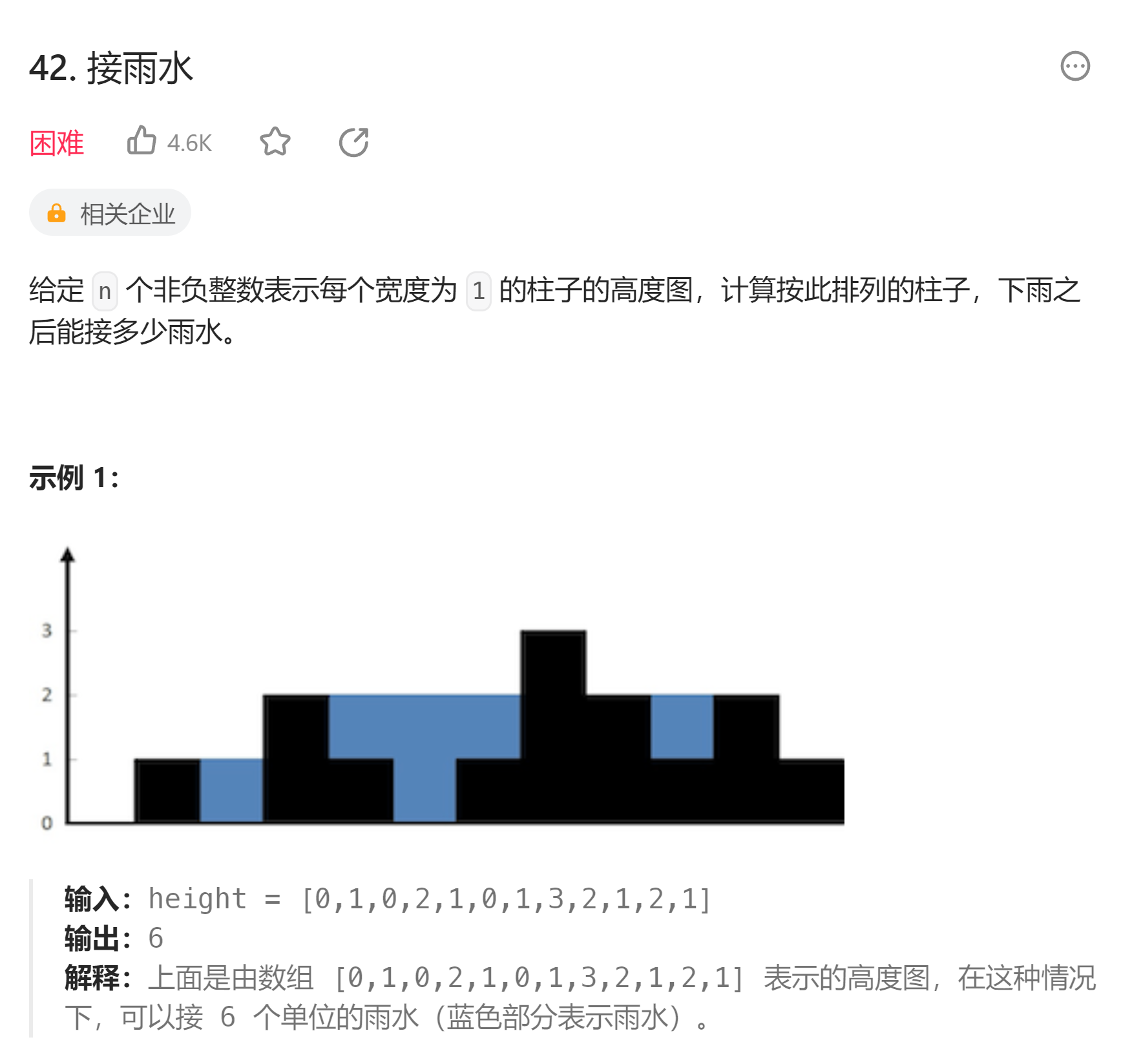
- 暴力双指针


- 双指针
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int length = height.length;
if (length <= 2) return 0;
int[] maxLeft = new int[length];
int[] maxRight = new int[length];
// 记录每个柱子左边柱子最大高度
maxLeft[0] = height[0];
for (int i = 1; i< length; i++) maxLeft[i] = Math.max(height[i], maxLeft[i-1]);
// 记录每个柱子右边柱子最大高度
maxRight[length - 1] = height[length - 1];
for(int i = length - 2; i >= 0; i--) maxRight[i] = Math.max(height[i], maxRight[i+1]);
// 求和
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int count = Math.min(maxLeft[i], maxRight[i]) - height[i];
if (count > 0) sum += count;
}
return sum;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
- 单调栈


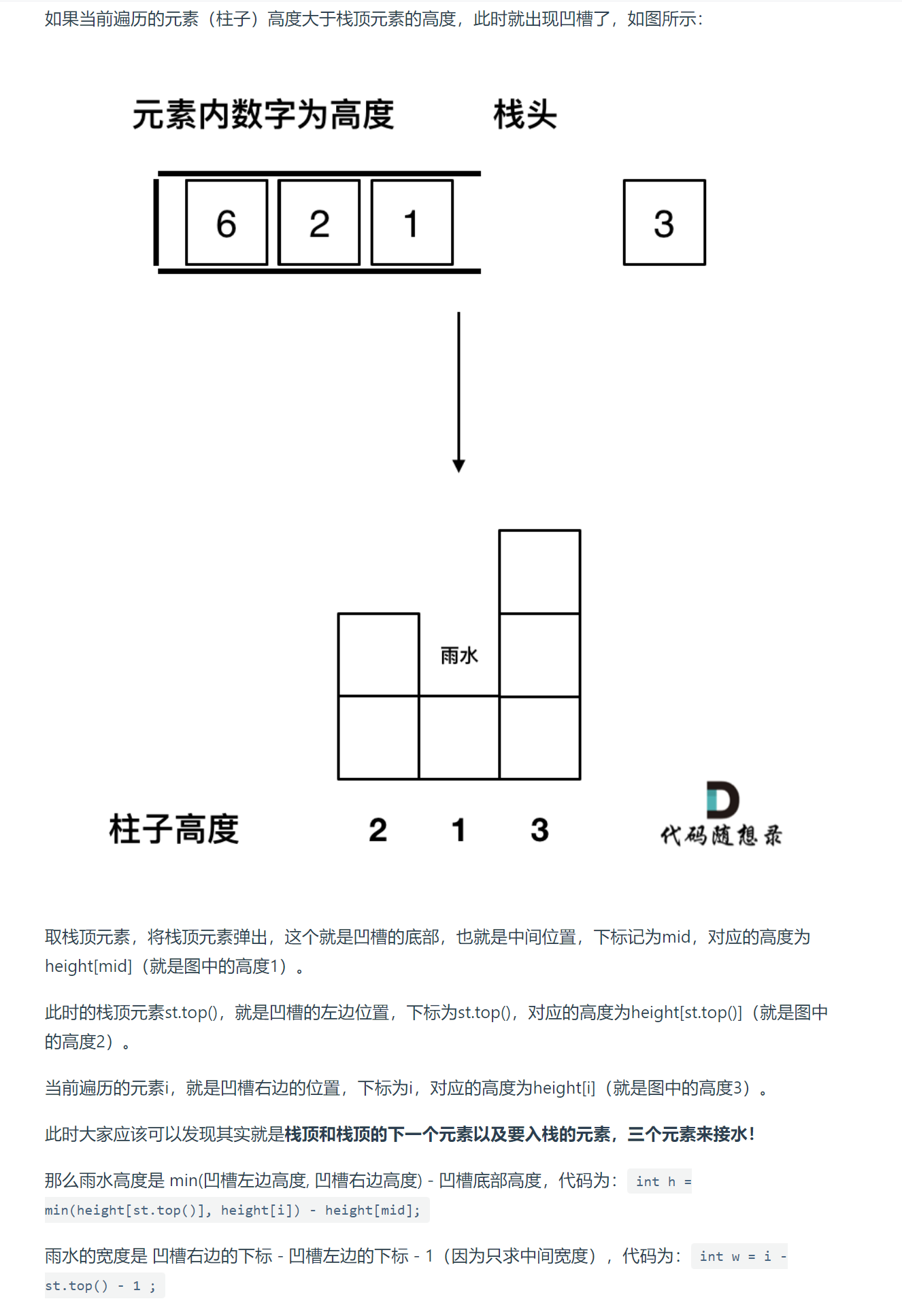
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height){
int size = height.length;
if (size <= 2) return 0;
// in the stack, we push the index of array
// using height[] to access the real height
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(0);
int sum = 0;
for (int index = 1; index < size; index++){
int stackTop = stack.peek();
if (height[index] < height[stackTop]){
stack.push(index);
}else if (height[index] == height[stackTop]){
// 因为相等的相邻墙,左边一个是不可能存放雨水的,所以pop左边的index, push当前的index
//不pop更好理解
//stack.pop();
stack.push(index);
}else{
//pop up all lower value
int heightAtIdx = height[index];
while (!stack.isEmpty() && (heightAtIdx > height[stackTop])){
int mid = stack.pop();
if (!stack.isEmpty()){
int left = stack.peek();
int h = Math.min(height[left], height[index]) - height[mid];
int w = index - left - 1;
int hold = h * w;
sum += hold;
stackTop = stack.peek();
}
}
stack.push(index);
}
}
return sum;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# 84. 柱状图中最大的矩形 (opens new window)
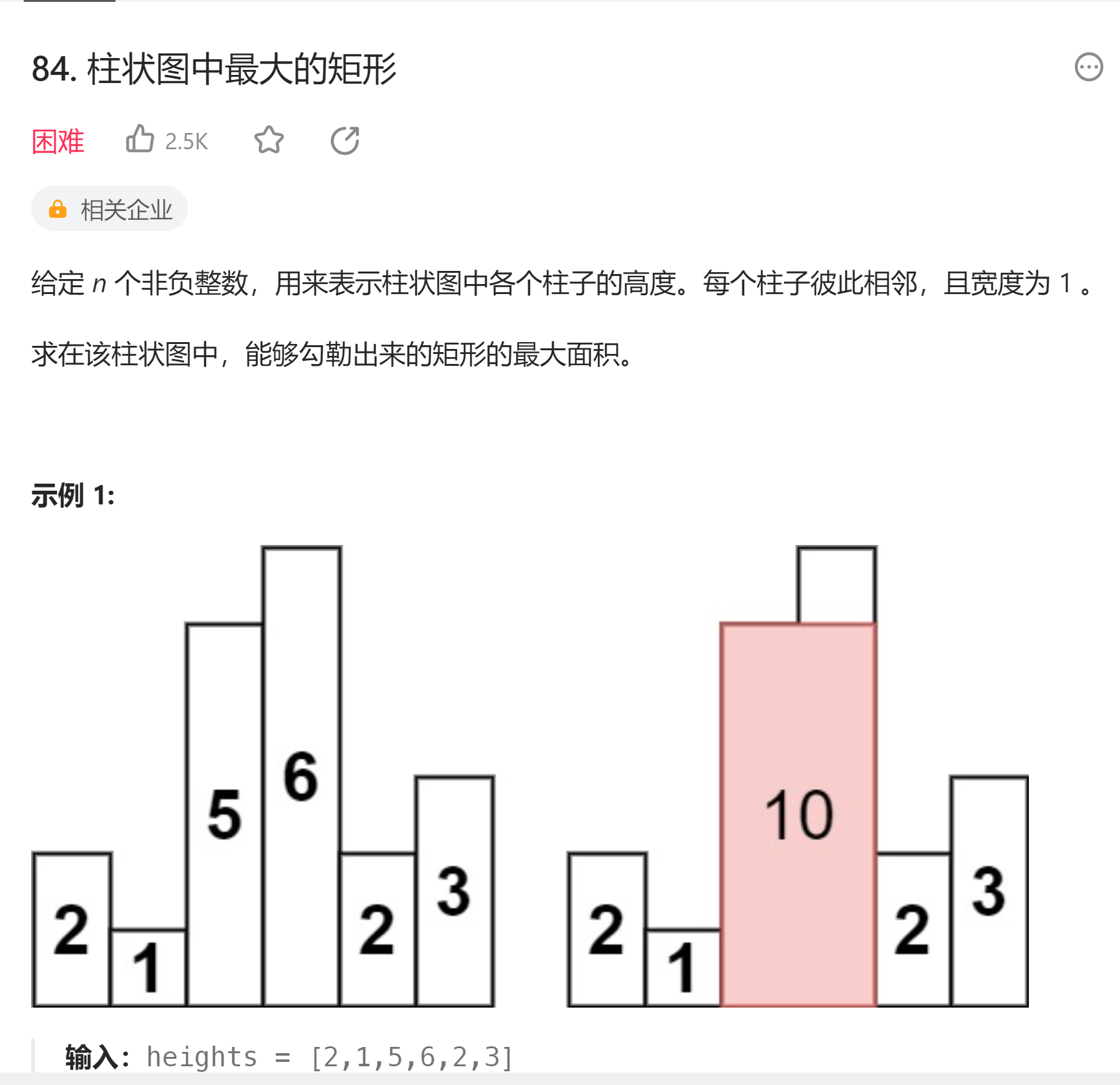
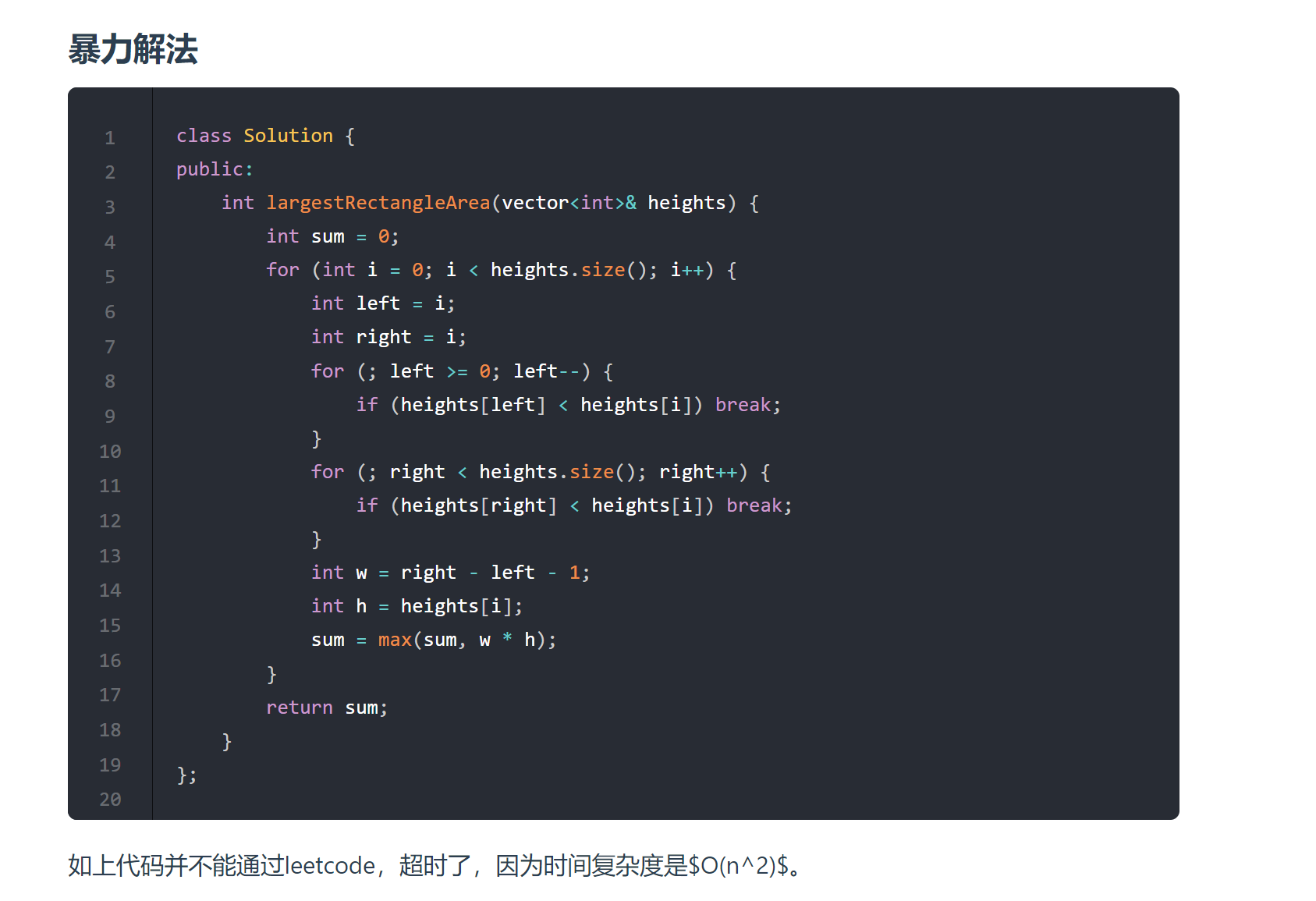
- 双指针
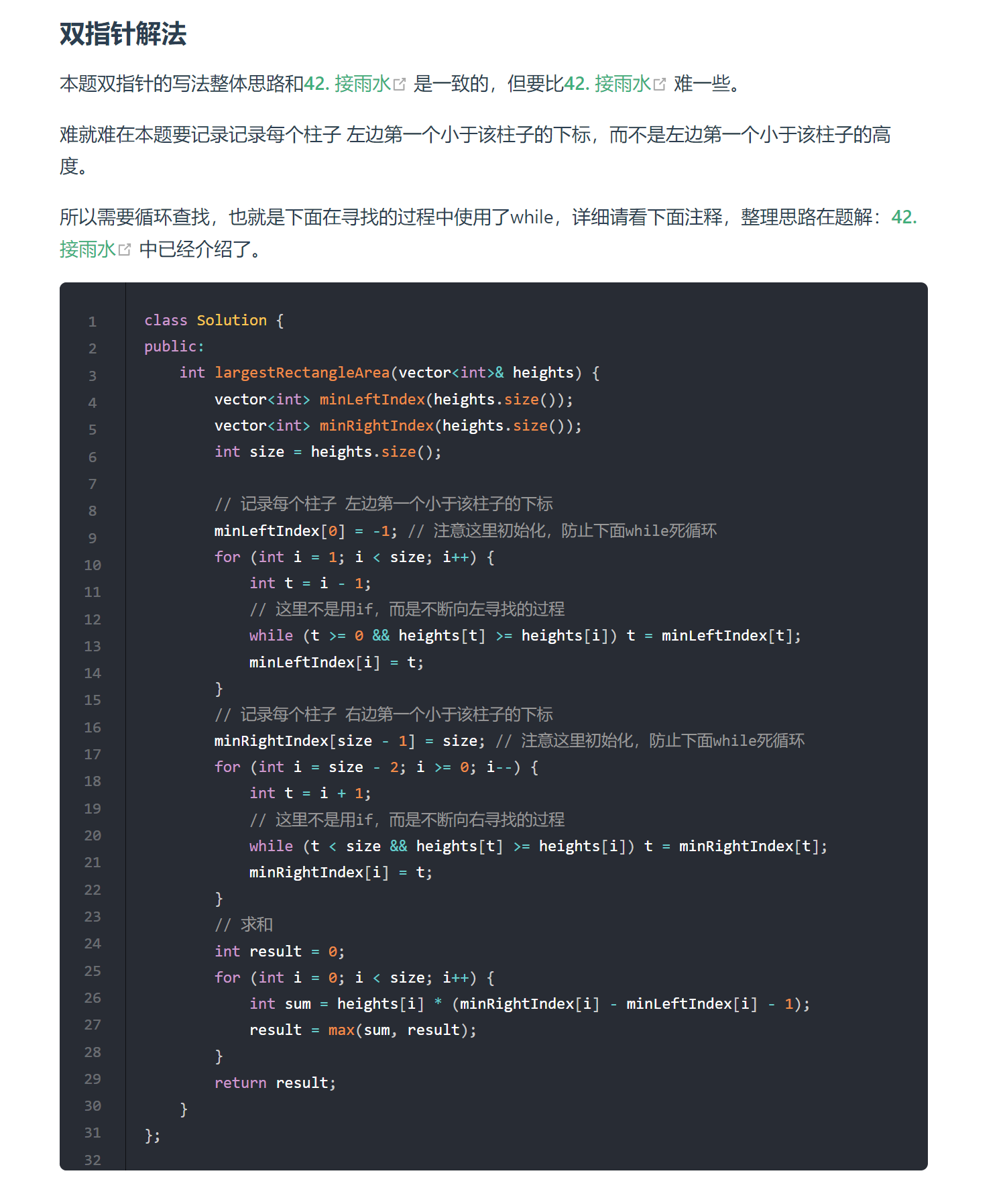
- 单调栈,注意前后加0

class Solution {
int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<Integer>();
// 数组扩容,在头和尾各加入一个元素
int [] newHeights = new int[heights.length + 2];
newHeights[0] = 0;
newHeights[newHeights.length - 1] = 0;
for (int index = 0; index < heights.length; index++){
newHeights[index + 1] = heights[index];
}
heights = newHeights;
st.push(0);
int result = 0;
// 第一个元素已经入栈,从下标1开始
for (int i = 1; i < heights.length; i++) {
// 注意heights[i] 是和heights[st.top()] 比较 ,st.top()是下标
if (heights[i] > heights[st.peek()]) {
st.push(i);
} else if (heights[i] == heights[st.peek()]) {
st.pop(); // 这个可以加,可以不加,效果一样,思路不同
st.push(i);
} else {
//mid是栈顶元素, right 不变, left 一直向左找,并存结果
while (heights[i] < heights[st.peek()]) { // 注意是while
int mid = st.peek();
st.pop();
int left = st.peek();
int right = i;
int w = right - left - 1;
int h = heights[mid];
result = Math.max(result, w * h);
}
st.push(i);
}
}
return result;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
