Ch02 Basics
#
# 2. 基本常用命令
# 2.1 数据库操作
默认保留的数据库
- admin: 从权限角度考虑, 这是
root数据库, 如果将一个用户添加到这个数据库, 这个用户自动继承所有数据库的权限, 一些特定的服务器端命令也只能从这个数据库运行, 比如列出所有的数据库或者关闭服务器 - local: 数据永远不会被复制, 可以用来存储限于本地的单台服务器的集合 (部署集群, 分片等)
- config: Mongo 用于分片设置时,
config数据库在内部使用, 用来保存分片的相关信息
$ show dbs $ use articledb $ show dbs1
2
3
4
5
6当使用
use articledb的时候.articledb其实存放在内存之中, 当articledb中存在一个 collection 之后, mongo 才会将这个数据库持久化到硬盘之中.
# 2.2 文档基本 CRUD
官方文档: https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/crud/
# 2.2.1 创建 Create
Create or insert operations add new documents (opens new window) to a collection (opens new window). If the collection does not currently exist, insert operations will create the collection automatically.
- 使用
db.<collection_name>.insertOne()向集合中添加一个文档, 参数一个 json 格式的文档 - 使用
db.<collection_name>.insertMany()向集合中添加多个文档, 参数为 json 文档数组
db.dropDatabase() //删除数据库
db.createCollection("my") //创建collection
show collections
2
3
db.collection.insert({
<document or array of documents>,
writeConcern: <document>,
ordered: <boolean>
})
// 向集合中添加一个文档
db.collection.insertOne(
{ item: "canvas", qty: 100, tags: ["cotton"], size: { h: 28, w: 35.5, uom: "cm" } }
)
// 向集合中添加多个文档
db.collection.insertMany([
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, tags: ["blank", "red"], size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } },
{ item: "mat", qty: 85, tags: ["gray"], size: { h: 27.9, w: 35.5, uom: "cm" } },
{ item: "mousepad", qty: 25, tags: ["gel", "blue"], size: { h: 19, w: 22.85, uom: "cm" } }
])
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
注:当我们向 collection 中插入 document 文档时, 如果没有给文档指定 _id 属性, 那么数据库会为文档自动添加 _id field, 并且值类型是 ObjectId(blablabla), 就是文档的唯一标识, 类似于 relational database 里的 primary key
- mongo 中的数字, 默认情况下是 double 类型, 如果要存整型, 必须使用函数
NumberInt(整型数字), 否则取出来就有问题了- 插入当前日期可以使用
new Date()
如果某条数据插入失败, 将会终止插入, 但已经插入成功的数据不会回滚掉. 因为批量插入由于数据较多容易出现失败, 因此, 可以使用 try catch 进行异常捕捉处理, 测试的时候可以不处理.如:
try {
db.comment.insertMany([
{"_id":"1","articleid":"100001","content":"我们不应该把清晨浪费在手机上, 健康很重要, 一杯温水幸福你我 他.","userid":"1002","nickname":"相忘于江湖","createdatetime":new Date("2019-0805T22:08:15.522Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(1000),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"2","articleid":"100001","content":"我夏天空腹喝凉开水, 冬天喝温开水","userid":"1005","nickname":"伊人憔 悴","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-05T23:58:51.485Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(888),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"3","articleid":"100001","content":"我一直喝凉开水, 冬天夏天都喝.","userid":"1004","nickname":"杰克船 长","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T01:05:06.321Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(666),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"4","articleid":"100001","content":"专家说不能空腹吃饭, 影响健康.","userid":"1003","nickname":"凯 撒","createdatetime":new Date("2019-08-06T08:18:35.288Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(2000),"state":"1"},
{"_id":"5","articleid":"100001","content":"研究表明, 刚烧开的水千万不能喝, 因为烫 嘴.","userid":"1003","nickname":"凯撒","createdatetime":new Date("2019-0806T11:01:02.521Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(3000),"state":"1"}
]);
} catch (e) {
print (e);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 2.2.2 查询 Read
- 使用
db.<collection_name>.find()方法对集合进行查询, 接受一个 json 格式的查询条件. 返回的是一个数组 db.<collection_name>.findOne()查询集合中符合条件的第一个文档, 返回的是一个对象

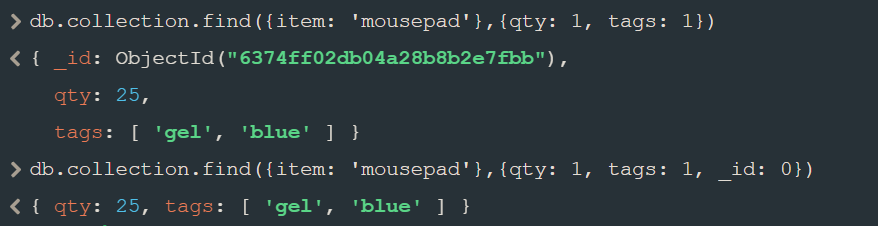
- 表示只显示name和address,要是不需要显示的字段就:0
可以使用 $in 操作符表示范围查询
db.inventory.find( { status: { $in: [ "A", "D" ] } } )
多个查询条件用逗号分隔, 表示 AND 的关系
db.inventory.find( { status: "A", qty: { $lt: 30 } } )
等价于下面 sql 语句
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" AND qty < 30
使用 $or 操作符表示后边数组中的条件是OR的关系
db.inventory.find( { $or: [ { status: "A" }, { qty: { $lt: 30 } } ] } )
等价于下面 sql 语句
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" OR qty < 30
联合使用 AND 和 OR 的查询语句
db.inventory.find( {
status: "A",
$or: [ { qty: { $lt: 30 } }, { item: /^p/ } ]
} )
2
3
4
在 terminal 中查看结果可能不是很方便, 所以我们可以用 pretty() 来帮助阅读
db.inventory.find().pretty()
匹配内容,例子:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_49485080/article/details/117651217
- 用. 操作符的时候记得加引号
db.posts.find({
comments: {
$elemMatch: {
user: 'Harry Potter'
}
}
}).pretty()
// 正则表达式
db.<collection_name>.find({ content : /once/ })
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
创建索引
db.posts.createIndex({
{ title : 'text' }
})
// 文本搜索
// will return document with title "Post One"
// if there is no more posts created
db.posts.find({
$text : {
$search : "\"Post O\""
}
}).pretty()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 2.2.3 更新 Update
- 使用
db.<collection_name>.updateOne(<filter>, <update>, <options>)方法修改一个匹配<filter>条件的文档 - 使用
db.<collection_name>.updateMany(<filter>, <update>, <options>)方法修改所有匹配<filter>条件的文档 - 使用
db.<collection_name>.replaceOne(<filter>, <update>, <options>)方法替换一个匹配<filter>条件的文档 db.<collection_name>.update(查询对象, 新对象)默认情况下会使用新对象替换旧对象
其中 <filter> 参数与查询方法中的条件参数用法一致.
如果需要修改指定的属性, 而不是替换需要用“修改操作符”来进行修改
$set修改文档中的指定属性
其中最常用的修改操作符即为$set和$unset,分别表示赋值和取消赋值.
db.inventory.updateOne(
{ item: "paper" },
{
$set: { "size.uom": "cm", status: "P" },
$currentDate: { lastModified: true }
}
)
db.inventory.updateMany(
{ qty: { $lt: 50 } },
{
$set: { "size.uom": "in", status: "P" },
$currentDate: { lastModified: true }
}
)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
- uses the
$set(opens new window) operator to update the value of thesize.uomfield to"cm"and the value of thestatusfield to"P",- uses the
$currentDate(opens new window) operator to update the value of thelastModifiedfield to the current date. IflastModifiedfield does not exist,$currentDate(opens new window) will create the field. See$currentDate(opens new window) for details.
db.<collection_name>.replaceOne() 方法替换除 _id 属性外的所有属性, 其<update>参数应为一个全新的文档.
db.inventory.replaceOne(
{ item: "paper" },
{ item: "paper", instock: [ { warehouse: "A", qty: 60 }, { warehouse: "B", qty: 40 } ] }
)
2
3
4
批量修改
// 默认会修改第一条
db.document.update({ userid: "30"}, { $set: {username: "guest"} } )
// 修改所有符合条件的数据
db.document.update( { userid: "30"}, { $set: {username: "guest"} } , {multi: true} )
2
3
4
5
列值增长的修改
如果我们想实现对某列值在原有值的基础上进行增加或减少, 可以使用 $inc 运算符来实现
db.document.update({ _id: "3"}, {$inc: {likeNum: NumberInt(1)}} })
# 修改操作符
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
$currentDate (opens new window) | Sets the value of a field to current date, either as a Date or a Timestamp. |
$inc (opens new window) | Increments the value of the field by the specified amount. |
$min (opens new window) | Only updates the field if the specified value is less than the existing field value. |
$max (opens new window) | Only updates the field if the specified value is greater than the existing field value. |
$mul (opens new window) | Multiplies the value of the field by the specified amount. |
$rename (opens new window) | Renames a field. |
$set (opens new window) | Sets the value of a field in a document. |
$setOnInsert (opens new window) | Sets the value of a field if an update results in an insert of a document. Has no effect on update operations that modify existing documents. |
$unset (opens new window) | Removes the specified field from a document. |
# 2.2.4 删除 Delete
- db.集合名称.remove(条件)
- db.集合名称.remove({}) 表示全部删除(不推荐使用)
- 使用
db.collection.deleteMany()方法删除所有匹配的文档. - 使用
db.collection.deleteOne()方法删除单个匹配的文档. db.collection.drop()db.dropDatabase()
db.inventory.deleteMany( { qty : { $lt : 50 } } )
Delete operations do not drop indexes, even if deleting all documents from a collection.
一般数据库中的数据都不会真正意义上的删除, 会添加一个字段, 用来表示这个数据是否被删除
# 2.3 文档排序和投影 (sort & projection)
# 2.3.1 排序 Sort
在查询文档内容的时候, 默认是按照 _id 进行排序
我们可以用 $sort 更改文档排序规则
{ $sort: { <field1>: <sort order>, <field2>: <sort order> ... } }
For the field or fields to sort by, set the sort order to 1 or -1 to specify an ascending or descending sort respectively, as in the following example:
db.users.aggregate(
[
{ $sort : { age : -1, posts: 1 } }
// ascending on posts and descending on age
]
)
2
3
4
5
6
# $sort Operator and Memory
# $sort + $limit Memory Optimization
When a $sort (opens new window) precedes a $limit (opens new window) and there are no intervening stages that modify the number of documents, the optimizer can coalesce the $limit (opens new window) into the $sort (opens new window). This allows the $sort (opens new window) operation to only maintain the top n results as it progresses, where n is the specified limit, and ensures that MongoDB only needs to store n items in memory. This optimization still applies when allowDiskUse is true and the n items exceed the aggregation memory limit (opens new window).
Optimizations are subject to change between releases.
有点类似于用 heap 做 topK 这种问题, 只维护 k 个大小的 heap, 会加速 process
举个栗子:
db.posts.find().sort({ title : -1 }).limit(2).pretty()
# 2.3.2 投影 Projection
有些情况, 我们对文档进行查询并不是需要所有的字段, 比如只需要 id 或者 用户名, 我们可以对文档进行“投影”
1- display0- dont display
> db.users.find( {}, {username: 1} )
> db.users.find( {}, {age: 1, _id: 0} )
2
3
# 2.4 forEach()
> db.posts.find().forEach(fucntion(doc) { print('Blog Post: ' + doc.title) })
# 2.5 其他查询方式
# 2.5.1 正则表达式(记得前后加斜杠)比如:包含 Yang的: /Yang/
$ db.collection.find({field:/正则表达式/})
$ db.collection.find({字段:/正则表达式/})
2
3
# 2.5.2 比较查询
<, <=, >, >= 这些操作符也是很常用的, 格式如下:
db.collection.find({ "field" : { $gt: value }}) // 大于: field > value
db.collection.find({ "field" : { $lt: value }}) // 小于: field < value
db.collection.find({ "field" : { $gte: value }}) // 大于等于: field >= value
db.collection.find({ "field" : { $lte: value }}) // 小于等于: field <= value
db.collection.find({ "field" : { $ne: value }}) // 不等于: field != value
2
3
4
5
# 2.5.3 包含查询
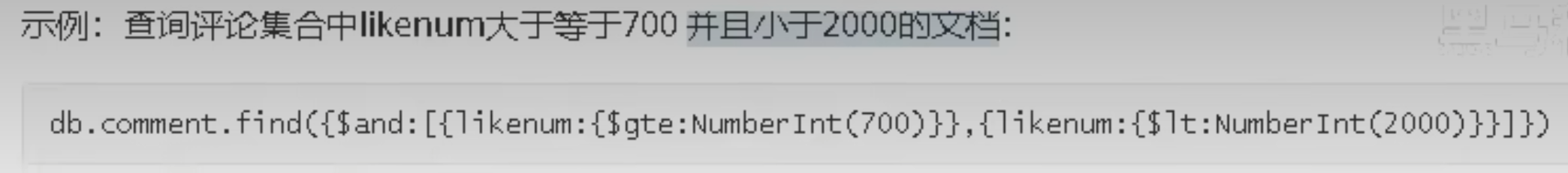
包含使用 $in 操作符. 示例:查询评论的集合中 userid 字段包含 1003 或 1004的文档
db.comment.find({userid:{$in:["1003","1004"]}})
不包含使用 $nin 操作符. 示例:查询评论集合中 userid 字段不包含 1003 和 1004 的文档
db.comment.find({userid:{$nin:["1003","1004"]}})
# 2.6 常用命令小结
选择切换数据库:use articledb
插入数据:db.comment.insert({bson数据})
查询所有数据:db.comment.find();
条件查询数据:db.comment.find({条件})
查询符合条件的第一条记录:db.comment.findOne({条件})
查询符合条件的前几条记录:db.comment.find({条件}).limit(条数)
查询符合条件的跳过的记录:db.comment.find({条件}).skip(条数)
修改数据:db.comment.update({条件},{修改后的数据})
或
db.comment.update({条件},{$set:{要修改部分的字段:数据})
修改数据并自增某字段值:db.comment.update({条件},{$inc:{自增的字段:步进值}})
删除数据:db.comment.remove({条件})
统计查询:db.comment.count({条件})
模糊查询:db.comment.find({字段名:/正则表达式/})
条件比较运算:db.comment.find({字段名:{$gt:值}})
包含查询:db.comment.find({字段名:{$in:[值1, 值2]}})
或
db.comment.find({字段名:{$nin:[值1, 值2]}})
条件连接查询:db.comment.find({$and:[{条件1},{条件2}]})
或
db.comment.find({$or:[{条件1},{条件2}]})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 3. 文档间的对应关系
- 一对一 (One To One)
- 一对多 (One To Many)
- 多对多 (Many To Many)
举个例子, 比如“用户-订单”这个一对多的关系中, 我们想查询某一个用户的所有或者某个订单, 我们可以
var user_id = db.users.findOne( {username: "username_here"} )._id
db.orders.find( {user_id: user_id} )
2
